Cyazofamid 氰霜唑
Introduction: Cyazofamid is a fungicide used mainly for controlling Oomycete and Plasmodiophora diseases on potatoes and tomatoes. Its mode of action is through preventing foliar and soil action with some residual activity and Respiration inhibitor effects. It has a low aqueous solubility, is unlikely to leach to groundwater and is non-volatile. It is not persistent in soils or aquatic systems. Whilst it has a low mammalian toxicity there is some concern regarding its potential for bioaccumulation. It is a skin and eye irritant. It is moderately toxic to birds, most aquatic organisms, honeybees and earthworms.
Common name: Cyazofamid
Another name: (4-Chloro-2-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-5-p-tolylimidazole-1-sulfonamide); BAS 54500F; Cyamidazosulfamid; Cyazofamid; Docious; Fendazosulam; IKF 916; Mildicut; Ranman; etc.
Chemical name: 4-chloro-2-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-5-p-tolylimidazole-1-sulfonamide
Empirical formula: C13H13ClN4O2S
Structural formula:
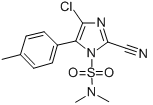
Mol. Weight: 324.78 g/mol
CAS No.: 120116-88-3
Specifications
Leading Cyazofamid supplier
Cyazofamid 95% TC
Cyazofamid 40% SC&GR
Cyazofamid 30% WP
Cyazofamid 20% SC
Cyazofamid 10% SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Cyazofamid FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5.5 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a sensitizer.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 17.1 mg/kg/day. Other No carcinogenic potential. Negative in Ames, REC assay, chromosomal aberration and mouse micronucleus tests.
ADI 0-0.17 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: NL (Not listed)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R50/53
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >2000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >0.14 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.19 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 0.025 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >151.7 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.75×10-8 mm Hg at 35℃ indicates cyazofamid will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase cyazofamid will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. If released to soil, cyazofamid is expected to have low to slight mobility based upon Koc values of 736-2172. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 3.9×10-7 atm-cu m/mole. Biodegradation half-lives in aerobic soil are reported as 3.7 to 6.4 days, indicating that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process. If released into water, cyazofamid is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Biodegradation half-lives of cyazofamid in aerobic aquatic environments were 14.7 to 18.0 days, aqueous anaerobic half-lives were 5.6 to 6.2 days. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 60 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate. Photodegradation of cyazofamid in aqueous systems has a reported half-life of 30 minutes. Hydrolysis half-lives of cyazofamid in aqueous environments averaged 11.9 days over a pH range of 4 to 9.
Usage: Cyazofamid was introduced by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. It is a broad spectrum foliar fungicide used to control a range of pathogens mainly on fruit.
Application: Biochemistry Both cyazofamid and the strobilurin fungicides inhibit at complex III (ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase) in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. However, cyazofamid inhibits Qi (the ubiquinone reducing site) of cytochrome bc1, whereas the strobilurins inhibit Qo (the ubiquinol oxidising site) of cytochrome bc1. Selectivity appears to be due to a difference in the susceptibility of the target enzyme Mode of action Foliar and soil preventative fungicide with residual activity and rainfastness, together with moderate translaminar and curative activity. Inhibits all stages in the lifecycle of Phytophthora infestans. Uses For control of Oomycete and Plasmodiophora diseases, such as potato and tomato late blight (Phytophthora infestans), downy mildews (e.g. of cucumber, Pseudoperonospora cubensis), at 60-100 g/ha. Its use as a foliar treatment on other crops, such as, vines, onions, lettuce, rice and crucifers is under investigation. Soil treatments are being evaluated for turf and crucifers.
| 






