PYRAZOSULFURON-ETHYL 吡嘧磺隆
Introduction: Mainly used to control broad-leaved weeds, grasses and sedges in rice.
Common name: Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl
Another name: Agreen, Sirius, Pyrazosulfuron ethyl, agreen(r), sirius(r), etc.
Chemical name: ethyl 5-[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]-1-methylpyrazole-4-carboxylate
Empirical formula: C14H18N6O7S
Structural formula:
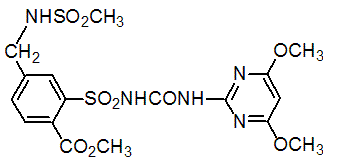
Mol. Weight: 414.29 g/mol
CAS No.: 93697-74-6
Specifications
Leading Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl supplier
Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl 10% WP
Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl 20% WP
Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl 75% WDG
Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
Not a hazardous substance or mixture.
Precautionary statement(s)
Not a hazardous substance or mixture.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for mouse: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 3.9 a.i.mg/L. 4) Not a skin irritant (rabbits). 5) Not a eye irritant (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: (78 w) for mice is 4.3 mg/kg daily.
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20/21/22 Xi - Irritant: R36/37/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50/53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 180 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 700 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedesmus acutus is 150 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 100 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 8000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: In rats, after 48 h, 80% of applied pyrazosulfuron-ethyl is excreted in urine and faeces. The major metabolic reaction is demethylation of the methoxy group. Soil/Environment: In soil, DT50 <15 d. In water, DT50 in buffer solution (pH 7), paddy fields or river water are c. 28 d.
Usage: Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl reported as a herbicide by S. Kobayashi (Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1989, No. 55, p. 17). Introduced by Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd in 1990. Manufacturers: JIE; Nissan; Sannong; Shenyang. Biochemistry: Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism (demethylation of methoxy group) in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)).
Application: Systemic herbicide, absorbed by roots and/or leaves and translocated to the meristems. Control of annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and sedges, pre- or post-emergence in wet-sown and transplanted rice crops, at 15-30 g/ha.
| 






