Thiodicarb 硫双威
Introduction: Thiodicarb is an insecticide and molluscicide used to control Lepidoptera, Coleoptera such as stem weevils, black beetles, springtails, caterpillars, cabbage white butterfly, budworms, tobacco loopers and slugs in Cereals including wheat, triticale, rye, barley, oats; Grapes; Forage brassicas; Grass seed crops; Cotton; Maize; Sweetcorn; Pulses; Tomatoes; Tobacco.
Common name: Thiodicarb
Another name: Dicarbasulf, Larvin, Bismethomyl thioether.
Chemical name: (3EZ,12EZ)-3,7,9,13-tetramethyl-5,11-dioxa-2,8,14-trithia-4,7,9,12-tetraazapentadeca-3,12-diene-6,10-dione
Empirical formula: C10H18N4O4S3
Structural formula:
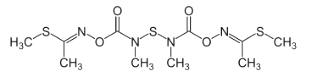
Mol. Weight: 354.47 g/mol
CAS No.: 59669-26-0
Specifications
Leading Thiodicarb supplier
Thiodicarb 80% WDG
Thiodicarb 96% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized Packing label
Thiodicarb FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301 (100%): Toxic if swallowed.
H330 (97.3%): Fatal if inhaled.
H400 (95.95%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 50 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >0.66 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly- irritating to eyes (rabbits). Thiodicarb, the active ingredient, has been shown not to be teratogenic or carcinogenic in animal studies. Two of the nine in vitro mutagenicity studies for this ingredient were positive, while an in vivo mutagenicity study in rats was negative. The weight of evidence suggests that thiodicarb is not a mutagen.
ADI: 0.03 mg/kg b.w.[2000]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R23, R25; Xn - Harmful: R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail >2023 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for sunfish is 1.4 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.027 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 8.3 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate to high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 3.1 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.153 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 38.5 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Thiodicarb's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide and molluscicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 4.3×10-5 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates thiodicarb will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase thiodicarb will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 9.7 days. Particulate-phase thiodicarb will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Thiodicarb contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and, therefore, may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, thiodicarb is expected to have moderate mobility based upon a Koc of 351. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces may be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.1×10-6 atm-cu m/mole. Thiodicarb is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Thiodicarb degrades rapidly in aerobic soil, with a reported half-life of 1.5 days in sandy loam soil, suggesting that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process in soil. Thiodicarb degrades rapidly into methomyl under most environmental conditions which is more mobile, persistent, and toxic than the parent compound. If released into water, thiodicarb may adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. The compound degrades under anaerobic conditions in aqueous environments with a reported half-life of 3 hours. Volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be a slow fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Estimated volatilization half-lives for a model river and model lake are 63 days and 1.3 years, respectively. A BCF of 5.7 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Thiodicarb has hydrolysis half-lives of 78 days, 32 days, and 12 hours at pH values of 5, 7, and 9, respectively. Occupational exposure to thiodicarb may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where thiodicarb is produced or used.
Usage: Thiodicarb was discovered by Vnion Carbide Agricultural Products Co., Inc and Ciba-Geigy AG.(Novartis Crop Protection AG) at almost the same time and developed by Vnion Carbide.
Application: Mode of action Insecticide with predominantly stomach action, but also limited contact action. As a seed treatment, rapidly translocated systemically through the plant. Molluscicide which provokes paralysis and death. Uses Control of all stages of major Lepidoptera and Coleoptera pests and some Hemiptera and Diptera on cotton, soya beans, maize, vines, fruit, vegetables, and many other crops, at 200-1000 g/ha; seed treatment rates are 2500-10 000 g/tonne. Also used as a molluscicide for control of slugs in cereals and oilseed rape.
| 






