METHOMYL
    灭多威 灭多威
Introduction: Systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of a wide range of insects (particularly Lepidoptera, Hemiptera, Homoptera, Diptera and Coleoptera) and spider mites in fruit, vines, olives, hops, vegetables, ornamentals, field crops, cucurbits, flax, cotton, tobacco, soya beans, etc. Also used for control of flies in animal and poultry houses and dairies. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as recommended, except to some varieties of apple.
Common name: Methomyl
Another name: Lan Bait
Chemical name: S-methyl (EZ)-N-(methylcarbamoyloxy)thioacetimidate
Empirical formula: C5H10N2O2S
Structural formula:
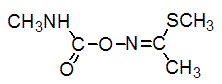
Mol. Weight: 162.21 g/mol
CAS No.: 16752-77-5
Specifications
Leading Methomyl supplier
Methomyl 200 g/L EC
Methomyl 25% WP
Methomyl 25% SP
Methomyl 90% WP
Methomyl 90% SP
Methomyl 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Methomyl FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H300: Fatal if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 30 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.215 a.i. mg/L. 4) non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) mild- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for rats is 100, mice is 50, dogs is 100 mg/kg diet.
ADI (JMPR): 0.02 mg/kg b.w.[2001]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): Ib (Highly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): I (oral, eye: Danger - Highly toxic), II (inhalation: Warning - Moderately toxic), III (dermal: Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: T+ - Very toxic: R28; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 24.2 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is 0.63 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.0076 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.16 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.28 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 19 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Methomyl's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 5.4×10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates methomyl will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase methomyl will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 58 hours. Particulate-phase methomyl will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Methomyl absorbs light greater than 290 nm and may undergo direct photolysis in the environment. The half-life for a thin film of methomyl exposed to laboratory lamps of environmentally significant wavelengths was 48.41 hours. If released to soil,methomyl is expected to have moderate mobility based upon a Koc of 160. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.9×10-11 atm-cu m/mole. Methomyl is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based on its vapor pressure. Methomyl biodegrades readily in soil with half-lives in the range of 3-14 days measured in 3 greenhouse soils and 5-6 weeks in tobacco growing soils. If released into water, methomyl is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Hydrolysis occurs slowly in water with half-lives of 56, 54, 38, and 20 weeks at pH's of 4.5, 6.0, 7.0, and 8.0, respectively. Based on its absorption of light greater than 290 nm, methomyl may undergo photolysis in sunlit surface waters, but the kinetics of this reaction are unknown. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Occupational exposure to methomyl may occur through inhalation of dust and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where methomyl is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to methomyl via ingestion of food products containing methomyl. (SRC)
Usage: Insecticide reported by G. A. Roodhans & N. B. Joy (Meded. Rijksfac. Landbouwwet. Gent, 1968, 33, 833). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. 'Lannate' was first marketed in 1967. Patents US 3576834; US 3639633 Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience; CAC; Crystal; Dow AgroSciences; DuPont; Hunan Linxiang; Jiangsu Eternal; Kuo Ching; Makhteshim-Agan; Rotam; Sinon.
Application: Methomyl 200 g/L EC can be used to control cotton bollworm, cotton aphid, thrips, et al. in cotton field at dosage of 90-120 mL/667 m2. 100-120 mL/667 m2 can be used to control cabbage caterpillar, Myzus persicae, plutella xylostella in vegetable field. 100-300 mL/667 m2 can be used to control geometrid moth, bean beetle, estigmene, leafhopper et al. in peanut and soybean field.
|