DICAMBA
  麦草畏 麦草畏
Introduction: A herbicide for control of annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and brush species such as bedstraw, buttercup, carpetwed, cocklebur, lambsquarters, mallow, goosefoot, pigweed, sowthistle, velvetleaf, knapweed, teasel, plantains, bindweed, thistles in corn, cotton, sugarcane, soybeans, sorghum, asparagus, grass seed crops and non-cropland field.
Common name: Dicamba
Another name: dicamba, Mdba, Mediben, Banvel, Dianat, Banlen, Brush buster, Banvel herbicide, etc.
Chemical name: 3,6-dichloro-o-anisic acid
Empirical formula: C8H6Cl2O3
Structural formula:
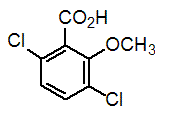
Mol. Weight: 221.04 g/mol
CAS No.: 1918-00-9
Specifications
Leading Dicamba supplier
Dicamba 420 g/L SC
Dicamba 480 g/L SL (dimethylamine salt)
Dicamba 97% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Dicamba FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H318: Causes serious eye damage.
H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 1581 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 4.46 a.i. mg/L. 4) Moderately irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Extremely irritating and corrosive to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 110 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs is 52 mg/kg b.w. daily. Developmental NOEL for rabbits is 30 mg/kg b.w. daily, rats is 160 mg/kg b.w. daily. Reproduction NOEL for rats is 50 mg/kg b.w. daily. Not mutagenic.
ADI(JMPR): 0.3 mg/kg b.w. [2010]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22, R41; N - Dangerous for the environment: R52, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is 1373 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >41.0 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 1.8 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Dicamba's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a registered herbicide for post emergent control of broadleaf weeds and woody plants will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.25×10-5 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates dicamba will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase dicamba will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5.4 days. Particulate-phase dicamba will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. A loss of 41% following continuous exposure of a natural water solution of dicamba to an artificial UV light (320 nm) for 133 days suggests that dicamba may be susceptible to direct photolysis in the atmosphere by sunlight. If released to soil, dicamba is expected to have very high mobility based upon experimentally-determined Koc values of 7 to 34. Literature reviews of dicamba adsorption and leaching in soil indicate the herbicide is highly mobile in most soil types. The pKa of dicamba is 1.97, indicating that this compound will exist almost entirely in the anion form in the environment and anions generally do not adsorb more strongly to soils containing organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts. Volatilization of dicamba from soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process; over a 154-day observation period, 0.6-7.9% of soil-applied dicamba volatilized. Although dicamba may leach readily in soil, the importance of leaching and volatilization can be attenuated by rapid aerobic biodegradation; microbial degradation is the most important process controlling the fate of dicamba in soil. Aerobic soil metabolism is the main degradative process with the formation of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid; metabolism in anaerobic soil is similar to aerobic soil (e.g. formation of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid) but slower. The persistence of dicamba in agricultural soils is highly variable and depends on factors such as application rates, moisture content, temperature, pH, soil type. Typical field dissipation half-lives can vary from 4.4 to 50 days under aerobic conditions with 18 days being an approximate median half-life. Under conditions amenable to rapid metabolism, the half-life is <14 days. Under anaerobic conditions, soil half-lives of 58 to 141 days have been observed. If released into water, dicamba is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Microbial degradation appears to be the most important removal process in natural water. In nonsterile water, 16% of applied dicamba disappeared after 133 days, suggesting that biodegradation in water may be an important environmental fate process. Dicamba did not bioaccumulate in algae, clam, crab, daphnia, elodea, mosquito fish, mosquito larvae or snail over a 32-day test period in an aquatic ecosystem study, indicating that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Dicamba is stable to abiotic hydrolysis in water and photodegrades slowly in water. Occupational exposure to dicamba may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where dicamba produced or used (e.g., mixing, loading, or applying dicamba or by entering a previously treated site). Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to dicamba via inhalation of ambient air, ingestion of food and drinking water, and dermal contact with this compound. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicide reported by R. A. Darrow & R. H. Haas (Proc. South. Weed Conf., 14th, 1961, p. 202). Introduced by Velsicol Chemical Corp., later manufactured and marketed by Sandoz AG (now Syngenta AG). Now marketed in USA and Canada by BASF, and elsewhere by Syngenta. Synthetic auxin (acting like indolylacetic acid).
Application: Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with ready translocation throughout the plant via both the symplastic and apoplastic systems. Acts as an auxin-like growth regulator. Control of annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and brush species in cereals, maize, sorghum, sugar cane, asparagus, perennial seed grasses, turf, pastures, rangeland, and non-crop land. Used in combinations with many other herbicides. Dosage varies with specific use and ranges from 0.1 to 0.4 kg/ha for crop use, higher rates in pasture. Phytotoxicity Most legumes are sensitive.
|