Fenhexamid 环酰菌胺
Introduction: Fenhexamid is a locally systemic, protectant fungicide. Fenhexamid prevents fungi from infecting plants by inhibiting spore germination and mycelial growth. The fungicide is absorbed into the outer waxy layer of plant surfaces and is protected from being washed off by rainfall or irrigation. Used for control of Botrytis diseases on grapes, greenhouse tomatoes, ornamentals and berry crops, including blackberries, blueberries, currants, loganberries, raspberries and strawberries; and Monilinia brown rot on cherries, peaches and nectarines.
Common name: Fenhexamid
Another name: Elevate; Teldor; N-(2,3-Dichloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1- methylcyclohexanecarboxamide; Fenhexamide; KBR 2738; Decree; etc.
Chemical name: 2',3'-dichloro-4'-hydroxy-1-methylcyclohexanecarboxanilide
Empirical formula: C14H17Cl2NO2
Structural formula:
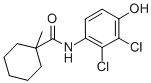
Mol. Weight: 302.20 g/mol
CAS No.: 126833-17-8
Specifications
Leading Fenhexamid supplier
Fenhexamid 98% TC
Fenhexamid 50% WDG&SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Fenhexamid FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H411 (100%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5.1 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitizer.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 28 mg/kg/day; (104 w) for mice is 247 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 17.4 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.2 mg/kg b.w. [2005]
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R51, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >804.4 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 1.34 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >18.8 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedesmus subcapitata is >26.1 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >102.07 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >500 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
All data indicate that there is no danger to the consumer from fenhexamid residues. Animals In rats, rapidly absorbed and eliminated without accumulation within 48 h. The major elimination followed the faecal route (61%), whereas renal excretion accounted for 15-36% of the total administered dose. Plants The metabolic pathway is similar in all crops; in all plant samples, the unchanged active ingredient was identified as the largest single constituent. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil £1 d (4 soils, 20 °C). Studies and calculation show that the compound can be classified as having no, or only low, leaching potential; no problems of groundwater contamination will be expected. In sterile aquatic systems, fenhexamid was stable to hydrolysis. In natural water/sediment systems, fenhexamid degrades rapidly and completely, ultimately forming CO2; overall DT50 (calc.) was a few days.
Usage: Fenhexamid was introduced by Bayer AG. It is a foliar fungicide used to control Botrytis spp. and some other pathogens in fruit, vegetables and ornamentals.
Application: Biochemistry Biochemical target is sterol biosynthesis (SBI class III), acting on 3-keto-reductase during C4-demethylation, displaying a low to moderate risk for resistance development. Inhibits germ tube elongation and mycelium growth. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protectant action; not translocated. Uses For control of Botrytis cinerea, Monilia spp. and related pathogens in grapes, berries, stone fruit, citrus, vegetables and ornamentals, at 500-1000 g/ha.
| 






