Diazinon
  二嗪磷 二嗪磷
Introduction: Diazinon is a non-systemic organo-phosphate insecticide used on home gardens and farms to control a wide variety of sucking and leaf eating insects. It is used on rice, fruit trees, sugarcane, corn, tobacco, potatoes and on horticultural plants. It is also an ingredient in pest strips. Diazinon has veterinary uses against fleas and ticks. Nearly 2.6 million pounds of diazinon were used each year prior to 1983. Some of the older formulations of diazinon were unstable and contained a number of potent impurities such as sulfotepp and monothiono-TEEP. Newer products do not contain impurities which increase the risk associated with diazinon use. In 1988 EPA cancelled the registration of diazinon for use on golf courses and sod farms. They cited die-offs of birds which often congregate in these areas.
Common name: Diazinon
Another name: Spectracide, AG500, Alfa-tox, Sarolex, D-Z-N Diazinon 14G,Geigy Spectracide Lawn and Garden Insect Control, etc.
Chemical Name (IUPAC) :O, O-diethyl-O-(2-isopropyl-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl) phosphorothioate
Structural formula:
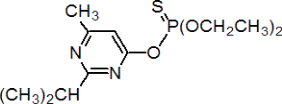
Empirical formula:C12H21N2O3PS
Mol. Weight: 304.3
CAS No.: 333-41-5
Specifications
Leading Diazinon supplier
Diazinon 95%TC
Diazinon 600g//L EC
Diazinon 500g/L EC
Diazinon 5% GR
Diazinon 10% GR
Packing
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Diazinon FAO standard
Professional registration
Customerized Packing label
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION:
GHS Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral]
H312: Harmful in contact with skin [Warning Acute toxicity, dermal]
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin]
H332: Harmful if inhaled [Warning Acute toxicity, inhalation]
H350: May cause cancer [Danger Carcinogenicity]
H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity]
H370: Causes damage to organs [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure]
H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [DangerSpecific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure]
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [WarningSpecific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure]
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard]
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard]
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70, 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats 1250, mice 80-135, guinea pigs 250-355 mg/kg; 2) Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2150, rabbits 540-650 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4h) for rats: >2.33 mg/L; 4) Skin irritation: Not an irritant (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation for rabbit: Minimally irritating; 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: not a sensitiser.
ADI (JMPR) 0.002 mg/kg b.w. [1993, 2001].
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22, N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53.
US EPA Classification (formulation): II, III (Warning - Moderately toxic, Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout 38.0 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna 40 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus quadricauda is 4.4 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute (48h) LD50 is >100 μg/bee, Oral acute (48h) LD50 is 100 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >5600 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 198 (WHO 1998), 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals The principal metabolites are diethyl thiophosphate and diethyl phosphate. Plants Studies with 14C-labelled diazinon show a rapid absorption and translocation in plants. Metabolism proceeds via hydrolysis and subsequent transformation and degradation of the hydroxypyrimidine derivatives to CO2. Soil/Environment Degradation involves oxidation to the phosphate (diazoxon) and hydrolysis (J. Pardue et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1970, 18, 405-408). DT50 c. 11-21 d (laboratory). Diazinon is fairly strongly adsorbed onto soil; Kom 332 mg/g o.m. Mobility is low.
Usage: Diazinon is a thiophosphoric acid ester developed in 1952 by Ciba-Geigy, a Swiss chemical company (later Novartis and thenSyngenta). Diazinon is used to control pest insects in soil, on ornamental plants, and on fruit and vegetable field crops.
Application: Diazinon is a non-systemic organophosphate insecticide. Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Uses Control of sucking and chewing insects and mites on a very wide range of crops, including deciduous fruit trees, citrus fruit, vines, olives, bananas, pineapples, vegetables, potatoes, beet, sugar cane, coffee, cocoa, tea, tobacco, maize, sorghum, alfalfa, flax, cotton, rice, ornamentals, glasshouse crops, forestry, etc., at 300-600g/ha; soil insects (by soil application); phorid and sciarid flies in mushroom cultivation; flies, lice, mites, fleas, cockroaches, bedbugs, ants, and other insect pests in animal houses and household use. Seed treatment for maize, for control of frit flies and also conferring bird-repellent properties. Also used as a veterinary ectoparasiticide.
|







