PROFENOFOS
    丙溴磷 丙溴磷
Introduction: Profenofos is an insecticide used on a wide variety of crops to control many pests but mainly Lepidoptera and mites. The example pests controlled is aphids, lygus bugs, cotton bollworm, tobacco bud worm, leaf webber, cotton leaf-perforator, beet armyworm, whitefly (suppression), spidermites, caterpillars. Profenofos is usually used in cotton, maize, tobacco, sugarbeet, soybeans, potatoes, ornamentals including jasmine.
Common name: Profenofos
Another name: Curacron, Selecron, Polycron, Profenophos.
Chemical name: (RS)-(O-4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate)
Empirical formula: C11H15BrClO3PS
Structural formula:
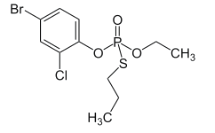
Mol. Weight: 373.63 g/mol
CAS No.: 41198-08-7
Specifications
Leading Profenofos supplier
Profenofos 500 g/L EC
Profenofos 720 g/L EC
Profenofos 90% TC
Profenofos 94% TC
Profenofos 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Profenofos FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P312: IF INHALED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 358 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: 472 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 3.0 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No adverse effects to workers of routine exposure to profenofos and no teratogenicity or carcinogenicity.
ADI: 0.03 mg/kg b.w.[2007]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification:Xn - Harmful: R20/21/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Coturnix japonica is 70 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.08 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.095 a.i.μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Profenofos' production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.00×10-7 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates profenofos will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase profenofos will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 8.6 hrs. Particulate-phase profenofos will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Profenofos is stable towards direct photolysis in water and on soil. If released to soil, profenofos is expected to have very low to slight mobility based upon a range of Koc values from 869 to 3,162. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.21×10-8 atm-cu m/mole. Profenofos metabolizes rapidly in alkaline aerobic conditions with a half-life of 2 days. The rate of metabolism is influenced by chemical hydrolysis; aerobic metabolism in neutral and acid conditions is likely to be slower. Profenofos also metabolizes rapidly in alkaline anaerobic conditions with a half-life of 3 days. If released into water, profenofos is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the range of Koc values. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. A range of BCF values in fish of 29 to 682 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate to high. Hydrolysis half-lives of profenofos are 104-108 days, 24-62 days, and 0.33 days for pHs 5,7, and 9, respectively. Occupational exposure to profenofos may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where profenofos is produced or used. The general population may be exposed to profenofos near agricultural areas where it is used as a pesticide.
Usage: Profenofos was developed by Novartis Crop Protection in 1975. Profenofos can be used on a variety of crops including cotton and vegetables such as maize, potato, soybean, and sugar beet. It was first registered in the United States in 1982. In the United States it is used exclusively on cotton and is primarily used against lepidopteran insects.
Application: Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Exhibits a translaminar effect. Has ovicidal properties. Control of insects (particularly Lepidoptera) and mites on cotton, maize, sugar beet, soya beans, potatoes, vegetables, tobacco, and other crops, at 250-1000 a.i.g/ha.
| 






