Fenoxycarb
    苯氧威 苯氧威
Introduction: Fenoxycarb is an insect specific growth regulator used to control moths, scale insects and other insects on olives, vines, cotton, various fruits, stored produce, ornamentals and turf. It is non-neurotoxic with contact and stomach action, acts by mimicing the action of the juvenile hormone keeping the insect in an immature state.
Common name: Fenoxycarb
Another name: Insegar, Varikill, Logic, Pictyl, Pyctyl, Torus
Chemical name: ethyl 2-(4-phenoxyphenoxy)ethylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C17H19NO4
Structural formula:
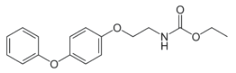
Mol. Weight: 301.34 g/mol
CAS No.: 79127-80-3
Specifications
Leading Fenoxycarb supplier
Fenoxycarb 50 g/L EC
Fenoxycarb 25% WP
Fenoxycarb 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Fenoxycarb FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H351 (73.58%): Suspected of causing cancer.
H400 (99.48%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity:
1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >10000 a.i.mg/kg.
2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg.
3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >4.4 a.i. mg/L.
4) non - irritating to skin (rabbits).
5) non- irritating to eyes (rabbits).
6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (18 mo) for mice is 5.5 mg/kg b.w.; (2 y) for rats is 8 mg/kg b.w.
ADI: 0.053 mg/kg b.w./day [Mouse, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; N-Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is >3000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish,
acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.66 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates,
acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for
Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 0.38 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour
LD50 is >204 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >204 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms,
acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >425 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Fenoxycarb's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insect growth regulator
will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 6.5×10-9 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates fenoxycarb
will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase fenoxycarb will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry
deposition. Fenoxycarbdoes not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible
to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, fenoxycarb is expected to have no mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 5,200.
Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant
of 4.3×10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Fenoxycarbis moderately persistent in soil with degradation following biphasic kinetics; the primary half-life for
aerobic degradation was 6.7 hours and the secondary value was 8.2 months using a sandy loam soil. If released into water, fenoxycarb is
expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Aerobic aquatic metabolism half-life of 3.9 days
in water alone and 18.8 days in a combined sediment and water system indicates that fenoxycarb is not expected to be persistent in water.
Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant.
An estimated bioconcentration factor of 400 suggests that the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. There has been no
observed photolysis for fenoxycarb in aqueous solutions, buffered to pH 6.5-10. Fenoxycarb is moderately stable in water with no evidence
of hydrolysis of fenoxycarb observed. Occupational exposure tofenoxycarb may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound
at workplaces where fenoxycarb is produced or used. Limited monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to fenoxycarb
via dermal contact with contaminated rain water containingfenoxycarb. (SRC).
Usage: Insecticide reported by S. Dorn et al. (Z. Pflanzenkr. Pflanzenschutz, 1981, 88, 269). Introduced by R. Maag Ltd (now Syngenta AG)
and first marketed in 1985. Patents EP 4334; US 4215139 to Roche. Manufacturers: Sannong; Syngenta.
Application: Fenoxycarb is a broad spectrum insect growth regulator. It is useful for control of fire ants, fleas, mosquitos, cockroaches, moths,
scale insects, and insects attacking vines, olives, cotton and fruit.
It mimics the action of the juvenile hormones (JH) on a number of physiological processes, such as molting and reproduction. Because of its ability
to imitate the physiological effects of juvenile hormones, it is often called a juvenile hormone analog (JHA). It exhibits ovicidal and ovolarvicidal activity against numerous insect species and affects its target species by exposing newly deposited eggs or very
early instars to high levels of simulated JH. FENOXYCARB binds to juvenile hormone receptor, but is not broken down by juvenile hormone esterases
in insect larvae. Since the insect is not usually exposed to high levels of JH until about halfway through embryonic development, its development is halted
and the eggs will not hatch. High levels of JHAs such as fenoxycarb, when applied to later instars,cause the final adult insect to maintain larval characteristics
and these insects generally can not reproduces.
| 






