Propoxur
    残杀威 残杀威
Introduction: Propoxur is a non-systemic insecticide which was introduced in 1959. Propoxur is not used on food crops. It is used against mosquitoes in outdoor areas, for flies in agricultural settings, for fleas and ticks on pets, as an acaricide, on lawns and turf for ants, on flowering plants, and in private dwellings and public buildings. It is also used as a molluscicide, a chemical that kills snails. It is effective against cockroaches, aphids and leafhoppe. Propoxur is one of the chemicals that have, to a large extent, replaced DDT in the control of black flies and mosquitoes. It is a nonsystemic insecticide with contact and stomach action that has longstanding residual poisonous, or toxic activity when it is in direct contact with the target pest. Many formulations are available including ready-to-use liquids and aerosols, emulsifiable concentrates, wettable powders, granular baits, dusts and impregnated pet collars and strips
Common name: Propoxur
Another name: Baygon; Aprocarb; Sendran; 2-Isopropoxyphenyl methylcarbamate; Propoxure; Propoxylor; Blattanex; Blattosep; Mrowkozol; Propotox; Suncide; Bolfo; Boruho; Brygou; etc.
Chemical name: 2-isopropoxyphenyl methylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C11H15NO3
Structural formula:
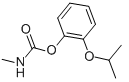
Mol. Weight: 209.24 g/mol
CAS No.: 114-26-1
Specifications
Leading Propoxur supplier
Propoxur 97% TC
Propoxur 98% TC
Propoxur 75% WP
Propoxur 20% EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Propoxur FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H320: Causes eye irritation.
H335: May cause respiratory irritation.
H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness.
H341: Suspected of causing genetic defects.
H351: Suspected of causing cancer.
H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
H370: Causes damage to organs.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >50 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >0.50 mg/l. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
Other No carcinogenic effects have been reported for propoxur. Not mutagenic in laboratory studies.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.02 mg/kg b.w.[1973, 1989]
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R25; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53.
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 25.9 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Bluegill sunfish is 6.2 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.15 mg/l. Effects on bees: acute (48 h) LD50 is >1.35 μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.68×10-6 mm Hg at 20℃ indicates propoxur will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase propoxur will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically- produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 12 hours. Particulate-phase propoxur will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. The photodegradation half-life in water was determined to be 88 hr when irradiated with light >290nm in water. If released to soil, propoxur is expected to have very high to high mobility based upon a Koc range of <1 to 103. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 3.35×10-9 atm-cu m/mole. Propoxur may not volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. The biodegradation of propoxur under aerobic conditions in silt loam and sandy loam soils followed first order kinetics for the first 112 and 180 days, resulting in half-life values of 80 days for the silt loam and 210 days for the sandy loam, respectively; this suggests that biodegradation is a moderate environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, propoxur is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Propoxur is reported to biodegrade quite rapidly in water, particularly when the bacterial activity and temperature are high. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 5 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is expected to be an important environmental fate process under neutral and basic conditions given half-lives of 1 yr at pH 4, 93 days at pH 7 and 30 hrs at pH 9.
Usage: Propoxur was developed by Baygon. It is a insecticide and acaricide active against a wide range of pests especially those that cause damage via sucking and chewing. Also used for flea control on domestic pets.
Application: Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Gives rapid knockdown, and has long residual activity. Uses Control of cockroaches, flies, fleas, mosquitoes, bugs, ants, millipedes and other insect pests in food storage areas, houses, animal houses, etc. Control of sucking and chewing insects (including aphids) in fruit, vegetables, ornamentals, vines, maize, alfalfa, soya beans, cotton, sugar cane, rice, cocoa, forestry, etc.; also against migratory locusts and grasshoppers.
| 






