Imidacloprid
    吡虫啉 吡虫啉
Introduction: Imidacloprid is a systemic insecticide which acts as an insect neurotoxin and belongs to a class of chemicals called the neonicotinoids which act on the central nervous system of insects with much lower toxicity to mammals. The chemical works by interfering with the transmission of stimuli in the insect nervous system. Specifically, it causes a blockage in the nicotinergic neuronal pathway. This blockage leads to the accumulation of acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter, resulting in the insect's paralysis, and eventually death. It is effective on contact and via stomach action. Because imidacloprid binds much more strongly to insect neuron receptors than to mammal neuron receptors, this insecticide is selectively more toxic to insects than mammals.
Common name: Imidacloprid
Another name: Admire; Confidor; Gaucho; Provado; 1-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl) methyl)-N-nitro-2-imidazolidinimine; Premise 75; etc.
Chemical Name (IUPAC): (E)-1-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-N-nitroimidazolidin-2-ylideneamine
Structural formula:
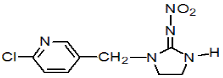
Empirical formula: C9H10ClN5O2
Mol. Weight: 255.66
CAS No.: 138261-41-3
Specifications
Leading Imidacloprid supplier
Imidacloprid 95% TC
Imidacloprid 98% TC
Imidacloprid 70% WP
Imidacloprid 70% WDG
Imidacloprid 25% WP
Imidacloprid 200g/L SL
Packing
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Imidacloprid FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302 Harmful if swallowed.
H400 Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264 Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P301 + P312 IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/physician if you feel unwell.
P330 Rinse mouth.
P501 Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local regulation.
Supplemental Hazard Statements none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 450 mg/kg. 2) Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5.323 mg/l dust, 0.069 mg/l air (aerosol). 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
NOEL (2 y) for male rats is 100 mg/kg diet, for female rats is 300 mg/kg diet, for mice is 330 mg/kg diet; NOEL (52 w) for dogs is 500 mg/kg diet. Other Not mutagenic or teratogenic.
ADI (JMPR) 0.06 mg/kg b.w. [2001].
Classification: WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is 31 mg/kg, for Bobwhite quail is 152 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for Bobwhite quail is 2225 mg/kg, for Mallard ducks is >5000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >83 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 85 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedemus subspicatus is >10 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute (48 h) LD50 is 0.081 μg/bee, Oral acute (48 h) LD50 is 0.0037 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 10.7 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration of methylene-14C- and 4,5-imidazolidine-14C- labelled imidacloprid to rats, the radioactivity was quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract and quickly eliminated (96% within 48 hours, mainly via the urine). Only c. 15% was eliminated as unchanged parent compound; the most important metabolic steps were hydroxylation at the imidazolidine ring, hydrolysis to 6-chloronicotinic acid, loss of the nitro group with formation of the guanidine and conjugation of the 6-chloronicotinic acid with glycine. All metabolites found in the edible organs and tissues of farm animals contained the 6-chloronicotinic acid moiety. Imidacloprid is also quickly largely eliminated from hens and goats. Plants Metabolism was investigated on rice (after soil treatment), maize (seed treatment), potatoes (granule or spray application), aubergines (granules) and tomatoes (spray treatment). In all cases, imidacloprid is metabolised by loss of the nitro group, hydroxylation at the imidazolidine ring, hydrolysis to 6-chloronicotinic acid and formation of conjugates; all metabolites contained the 6-chloropyridinylmethylene moiety. Soil/Environment In lab. studies, the most important metabolic steps were oxidation at the imidazolidine ring, reduction or loss of the nitro group, hydrolysis to 6-chloronicotinic acid and mineralisation; these processes were strongly accelerated by vegetation. Imidacloprid shows a medium adsorption to soil. Column leaching tests (with prior ageing) with a.i. and various formulations showed that imidacloprid and soil metabolites are to be classified as immobile; leaching into deeper soil layers is not to be expected if imidacloprid is used as recommended. Stable to hydrolysis under sterile conditions (under exclusion of light). Environmental DT50 c. 4 h (calc., based on tests of direct photolysis in aqueous solutions). Besides sunlight, the microbial activity of a water/sediment system is an important factor for the degradation of imidacloprid.
Usage: Imidacloprid was developed by Bayer Crop Science. It is widely used for pest control in agriculture. Other uses include application to foundations to prevent termite damage, pest control for gardens and turf, treatment of domestic pets to control fleas, protection of trees from boring insects,and in preservative treatment of some types of lumber products.
Application: Biochemistry Acts as an antagonist by binding to postsynaptic nicotinic receptors in the insect central nervous system. Mode of action Systemic insecticide with translaminar activity and with contact and stomach action. Readily taken up by the plant and further distributed acropetally, with good root-systemic action. Uses Control of sucking insects, including rice-, leaf- and planthoppers, aphids, thrips and whitefly. Also effective against soil insects, termites and some species of biting insects, such as rice water weevil and Colorado beetle. Has no effect on nematodes and spider mites. Used as a seed dressing, as soil treatment and as foliar treatment in different crops, e.g. rice, cotton, cereals, maize, sugar beet, potatoes, vegetables, citrus fruit, pome fruit and stone fruit. Applied at 25-100 g/ha for foliar application, and 50-175 g/100 kg seed for most seed treatments, and 350-700 g/100 kg cotton seed. Also used to controls fleas in dogs and cats.
| 






