FLUAZINAM
    氟啶胺 氟啶胺
Introduction: A protective broad spectrum fungicide used to control various soil-borne fungal pathogens including sclerotinia blight, late blight, white mould, clubroot, downy mildew, scab, alternaria blotch on a range of crops. It also has some acaricidal activity.
Common name: Fluazinam
Another name: Frowncide, Shirlan Flow, Shirlan (Zeneca), Fluazinam [ISO], Fluaziname, Altima, Mapro, Sekoya, shirlan(van)
Chemical name: 3-chloro-N-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl)-α,α,α-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-p-toluidine
Empirical formula: C13H4Cl2F6N4O4
Structural formula:
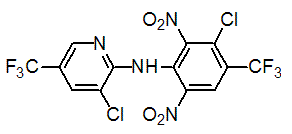
Mol. Weight: 465.14 g/mol
CAS No.: 79622-59-6
Specifications
Leading Fluazinam supplier
Fluazinam 500 g/L SC
Fluazinam 0.5% WP
Fluazinam 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Fluazinam FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H318: Causes serious eye damage.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H361d: Suspected of damaging the unborn child.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/ eye protection/ face protection.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P312: IF INHALED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: > 4100 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.463 a.i. mg/L. 4) slightly- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Tech. is a skin sensitiser, but purified material is not (guinea pigs). No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
ADI: 0.01 mg/kg b.w.[Mouse, SF=100]
Classification:
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available
EC Risk Classification: Reproduction risk category 3: R63; T - Toxic: R23; Xn - Harmful: R41, R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 1782 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is 0.055 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.22 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 96 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 0.16 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is > 500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Fluazinam's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as a fungicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 5.6×10-5 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates fluazinam will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase fluazinam will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 240 days. Particulate-phase fluazinam will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. This substance is expected to undergo direct photolysis based on a measured aquatic photolysis half-life of 2.5 days. If released to soil, fluazinam is expected to have slight to low mobility based upon measured Koc values ranging from 1,705 to 2,316. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.5×10-4 atm-cu m/mole. However, adsorption to soil is expected to attenuate volatilization. Fluazinam is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. The half-lives for the biodegradation of fluazinam in aerobic soil range from 9-49 days. Half lives for the biodegradation of fluazinam in anaerobic soil range from 4.5-32 days. If released into water, fluazinam is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the measured Koc values. The measured aerobic and anaerobic aquatic metabolism half-lives of fluazinam have both been reported to be less than or equal to 8 hours. Volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Estimated volatilization half-lives for a model river and model lake are 7 hours and 11 days, respectively. However, volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be attenuated by adsorption to suspended solids and sediment in thewater column. The estimated volatilization half-life from a model pond is 120 days if adsorption is considered. The pKa of fluazinam is 7.34, indicating that this compound will partially exist in cation form in the environment and cations generally adsorb more strongly to organic carbonand clay than their neutral counterparts. Measured BCF values of 348 to 1,850 suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high to very high.Fluazinam is expected to undergo hydrolysis in the environment based on measured half-lives of 42 days at pH 7 and 6 days at pH 9. The major hydrolysis product is 5-chloro-6-(3-chloro-alpha, alpha, alpha-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-p-toluidino)nicotinic acid. Occupational exposure to fluazinammay occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where fluazinam is produced or used. Exposure studies indicate that field workers may be exposed to fluazinam during mixing, loading, and application activities involving this substance. (SRC)
Usage: Fungicide discovered and introduced by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd and first marketed in 1990. Manufacturers: Ishihara Sangyo
Application: Uncouples mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, inhibiting spore germination, hyphal penetration, growth and sporulation. Fungicide with protective action. Has little curative or systemic activity, but good residual effect and rain fastness. Used to control of grey mould and downy mildew on vines; apple scab; southern blight and white mould on peanuts; and Phytophthora infestans and tuber blight on potatoes. Control of clubroot on crucifers, and rhizomania on sugar beet. Applied at 150-750 g/ha. Also for control of mites in apples.
| 






