FENTIN ACETATE
    三苯基醋酸锡, 薯瘟锡 三苯基醋酸锡, 薯瘟锡
Introduction:Fentin Acetate is a fungicide used to control a range of fungal infections including Phytophthora infestans, leafspot diseases, anthracnose on potatoes, sugarbeet, beans, rice, coffee, peanuts. It also has some molluscide and algicide activity.
Common name: Fentin Acetate
Another name: Phentin acetate, Phentinoacetate, Brestan, Acetoxytriphenylstannane, Fentinacetat, Lirostanol, Batasan, Liromatin, Tinestan, Stannane, (acetyloxy)triphenyl-Suzu, Fenolovo acetate, Tin triphenyl acetate, Triphenylaceto stannane, Acetatotriphenylstannane, Triphenyl-zinnacetat, Fentin acetaat, Fentin azetat, Fentine acetate, Fintin acetato, TPTA, TPZA, Phenostat A,Fentin acetat
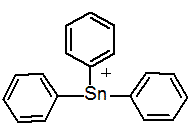
Chemical name: triphenyltin acetate
Empirical formula: C20H18O2Sn
Structural formula:
Mol. Weight: 410.07 g/mol
CAS No.: 900-95-8
Specifications
Leading Fentin Acetate supplier
Fentin Acetate 45% WP
Fentin Acetate 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized Packing label
Fentin Acetate FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H311: Toxic in contact with skin.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H318: Causes serious eye damage.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H335: May cause respiratory irritation.
H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
H370: Causes damage to organs.
H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P280: Wear protective gloves/ eye protection/ face protection.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P307+P311: IF exposed: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P361: Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 140 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: 127 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.044 a.i. mg/L. 4) Irritating to eyes (rabbit). 5) Irritant to skin and mucous membranes. 6) Sensitization possible through skin contact. NOEL: (2 y) for dogs is 4 mg/kg diet.
ADI(JMPR): 0.0005 mg/kg b.w. [1970]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; Reproduction risk category 3: R63; T+ - Very toxic: R26; T - Toxic: R24/25, R48/23, R41; Xi - Irritant: R37/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Phasianidae is 77.4 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Cyprinidae is 0.32 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.00032 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.0000027 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 16 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is >125 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Fentin acetate's production and former use as an agricultural fungicide and as a biocide in marine antifouling paints resulted in its release to the environment through various waste streams. If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of 4.8×10-7 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates Fentin Acetate will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase Fentin Acetate will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 2.7 days. Particulate-phase Fentin Acetate will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, Fentin Acetate is expected to have low mobility since triphenyltins are strongly adsorbed to soil. In moist soil and water, Fentin Acetate will dissociate to form triphenyltin oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, or hydrated cations; these species are not expected volatilize from moist soil orwater surfaces. If released into water, Fentin Acetate is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment. Fentin Acetate undergo biodegradation in the environment. Fentin Acetate degraded in normal, fertile, agricultural field at 11-16 deg C in <6 wks under aerobic conditions and 6-18 weeks under anaerobic conditions. A BCF of 800 for rainbow trout suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. Occupational exposure to Fentin Acetate may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces wheretriphenyltin acetate is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Fungicidal properties of organotin compounds investigated by G. J. M. van der Kerk & J. G. A. Luijten (J. Appl. Chem., 1954, 4, 314; 1956, 6, 56) and reviewed by H. Bock (Residue Rev., 1981, 79, 1). Fentin acetate was introduced by Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience) and fentin hydroxide by N.V. Philips-Duphar (now Crompton Corp.), both in 1959/1960.
Application: Multi-site inhibitor, preventing spore germination, and inhibiting metabolism of the fungal organism, in particular respiration. Non-systemic fungicide with mainly protective action, but also some curative action. Also acts as an algicide and molluscicide. Used to control of early and late blights of potatoes (at 200-300 g/ha), leaf spot diseases of sugar beet (at 200-300 g/ha), anthracnose of beans (at 200 g/ha). Phytotoxicity Vines, ornamentals, some fruits, and glasshouse crops may be injured.
| 






