BENOMYL
    苯菌灵 苯菌灵
Introduction: Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed through the roots and green tissues, with translocation acropetally. Acts by inhibiting development of the germ tubes, the formation of appressoria, and the growth of mycelia. Effective against a wide range of Ascomycetes, Fungi Imperfecti and some Basidiomycetes in cereals, grapes, pome and stone fruit, rice and vegetables. It is also effective against mites, primarily as an ovicide. Also used as pre-harvest spray or dip for the control of storage rots of fruit and vegetables.
Common name: Benomyl
Another name: Benlate, Fundazol, Agrocit, Uzgen, Fungochrom, Benlate 50, Arbortrine, Fundasol, Benomyl-Imex, Kribenomyl, Chinoin-fundazol, Benosan, Benex, Benomil, Fibenzol, Kribenomy, Benlat
Chemical name: methyl 1-(butylcarbamoyl)benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C14H18N4O3
Structural formula:
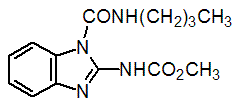
Mol. Weight: 290.32 g/mol
CAS No.: 17804-35-2
Specifications
Leading Benomyl supplier
Benomyl 500 g/L SC
Benomyl 50% WP
Benomyl 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Benomyl FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H316: Causes mild skin irritation.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H340: May cause genetic defects.
H360: May damage fertility or the unborn child.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P332+P313: IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat (male): >10000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 2.0 a.i. mg/L. 4) Negligible irritant to skin (rabbits). 5) Temporary irritant to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is >2500 mg/kg diet (maximum rate tested), no evidence of histopathological changes; for dogs is 500 mg/kg diet.
ADI (JMPR): 0.1 mg/kg b.w.[1995]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Mutagenic category 2: R46; Reproduction risk category 2: R60, R61; Xn - Harmful: R43; Xi - Irritant: R37, R38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Mallard ducks is 1000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.17 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.28 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedesmus acutus is 2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 10 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 10.5 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Benomyl's production and use as a fungicide will result in its direct release to the environment through various waste streams. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 3.7×10-9 mm Hg at deg C indicates benomyl will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase benomyl will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, benomyl is expected to have slight mobility based upon a Koc of 2,000. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 4.93×10-12 atm-cu m/mole. Benomyl is not expected to volatilize from dry soils based upon its vapor pressure. Biodegradation is not expected to be a major environmental fate process since benomyl hydrolyzes rapidly to methyl 2-benzimidazole carbamate (carbendazim; MBC) and butyl isocyanate in moist soil and water. The half-life of benomyl is 2 and 19 hours in water and soil, respectively. If released into water,benomyl is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 9 suggests potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Occupational exposure to benomyl may occur through inhalation of dust particles and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where benomyl is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to benomylvia ingestion of food products containing benomyl. (SRC)
Usage: Fungicide reported by C. J. Delp & H. L. Klopping (Plant Dis. Rep., 1968, 52, 95). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. in 1970, who ceased marketing it in 2001. Manufacturers: Agro-Chemie; Aragro; CAC; Gilmore; Jiangsu Eternal; Sannong; Sharda; Sinon; Sundat.
Application: Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed through the leaves and roots, with translocation principally acropetally. Effective against a wide range of Ascomycetes, and Fungi Imperfecti and some Basidiomycetes in cereals, grapes, pome and stone fruit, rice and vegetables. It is also effective against mites, primarily as an ovicide. Also used as pre-harvest sprays or dips for the control of storage rots of fruit and vegetables. Typical rates are: on field and vegetable crops, 140-550 g a.i./ha; on tree crops 550-1100 g/ha; for post-harvest uses 25-200 g/hl.
| 






