Chlorothalonil
   
Introduction: Chlorothalonil is a broad-spectrum organochlorine fungicide used to control fungi that threaten vegetables, trees, small fruits, turf, ornamentals, and other agricultural crops. It also controls fruit rots in cranberry bogs.
Common name: chlorothalonil
Another name: (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI); TPN (JMAF)
Chemical Name (IUPAC): 2,4,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,3-dicarbonitrile
Structural formula:
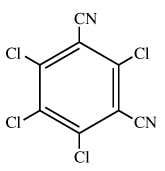
Empirical formula: C8Cl4N2
Mol. Weight: 265.9
CAS No.:1897-45-6
Specifications
Leading chlorothalonil supplier
chlorothalonil 98% TC
chlorothalonil 75% WP
Chlorothalonil 720g/L SC
chlorothalonil 500g/L SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
chlorothalonil FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION:
GHS Hazard statement(s)
Prevention:
P201 - Obtain special instructions before use
P202 - Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood
P260 - Do not breathe dust
P271 - Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area
P272 - Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace
P273 - Avoid release to the environment
P280 - Wear protective gloves, protective clothing, face protection, eye protection
Response:
P302+P352 - IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water
P304+P340 - IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing
P305+P351+P338 - IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing
P308+P313 - IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention
P310 - Immediately call a doctor, a POISON CENTER
P312 - Call a doctor, a POISON CENTER if you feel unwell
P320 - Specific treatment is urgent (see a doctor, a POISON CENTER on this label), P321 - Specific treatment (see a doctor, a POISON CENTER on this label) P333+P313 - If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention
P362+P364 - Take off contaminated clothing and wash it before reuse
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews CAG (see part 2 of Bibliography). IARC ref. 30; 73 class 2B. Acute toxicity: 1)Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg; 2) Acute percutaneous LD50 for albino rabbits >5000 mg/kg; 3) AcuteInhalation LC50 (1h) for rats 0.52 mg/l air; (4 h) for rats 0.10 mg/l air. 4) Skin irritation: Not an irritant (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation for rabbit: Moderately irritant; 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: not a sensitize.
Evidence in humans of contact dermatitis with repeated exposure. NOEL Chronic administration of chlorothalonil has been associated with renal hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis of the forestomach in the kidney and forestomach of rats and male mice. These pre-neoplastic lesions precede subsequent tumour development in the rodent kidney and forestomach. The mode of action has been demonstrated to be epigenetic with a NOEL of 1.8 in rats and 1.6 in mice. In dogs, the pattern of toxicity is different from that in rodents with no evidence of toxicity in the kidney or forestomach, and a NOEL of at least 3 mg/kg b.w. (JMPR 1994).
ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg [1994]; 0.02mg/kg[2009]; 0.02mg/kg[2010]; (EPA) 0.02 mg/kg (RED 1998),
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; T+ - Very toxic: R26; Xn - Harmful: R43, R41; Xi - Irritant: R37; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53US EPA Classification (formulation): II, III (Warning - Moderately toxic, Caution - Slightly toxic)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effects on Birds: low toxic to birds, Acute oral LD50 for Janpanses quail is >2000 a.i. mg/kg. Effects on Fish: high toxic to fish, LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout is 0.017 a.i. mg/l. Effects on Aquatic invertebrates: the LC50 for Dangna magna (48h) is 70 a.i. mg/l. Effects on Algae: high toxic to Algae, the EC50 (48h) for Daphnia magna is 210 a.i. mg/l. Effects on Algae: moderate toxic to algae, theEC50 (72h) for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 0.21 mg/l. Effects on Bees: Low toxic to honeybees, Acute contact LD50 (48h) for honeybees is > 101 a.i.μg/bee, Acute oral LD50(48h) for honeybees is >63 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on Earthworms: the LC50 (14d) is 268.5 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 183 (WHO, 1996) Animals Chlorothalonil is not well absorbed following oral dosing. It reacts with glutathione in the gut rumen, or immediately on absorption into the body, to give mono-, di- or tri- glutathione conjugates. These may be excreted through urine or faeces, or subject to further metabolism resulting in thiol or mercapturic acid derivatives. Excretion of these in urine is believed to be significantly greater in rats than in dogs or primates. In ruminants, the major identified metabolite is the the 4-hydroxy derivative; no parent material is found. Plants In plants the majority of residues remain as parent compound; 4-hydroxy-2,5,6 -trichloroisophthalonitrile is found as a metabolite to a limited extent. Soil/Environment Koc 1600 (sand) to 14000 (silt), indicating low mobility to immobile. In aerobic and anaerobic soil studies, DT50 is 0.3-28 d (20°C). Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5-7, at pH 9 (22 °C), DT50 is 38 d. Degradation is faster in biotic aquatic systems, typical DT50 (aerobic) <8 h, (anaerobic) <10 d. A wide variety of metabolites are formed which are in turn degraded further.
Usage: chlorothalonil is developed in Diamond Alkal i Co. It was first registered for use in the US in 1966. It is an organic compound mainly used as a broad spectrum, nonsystemic fungicide , with other uses as a wood protectant, pesticide, acaricide, and to control mold, mildew, bacteria, algae.
Application: Chlorothalonil’s mode of action involves its combination with a molecule called glutathione inside fungus cells. As these glutathione-chlorothalonil derivatives form, they tie up all of the cells’available glutathione, leaving enzymes glutathione-dependent unable to function. Several enzymes that are important in cellular respiration, the process by which large molecules are broken down and provide the cell with energy, are glutathionedependent. Their inhibition leads to chlorothalonil’s toxic effects. Uses Control of many fungal diseases in a wide range of crops, including pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, bush and cane fruit, cranberries, strawberries, pawpaws, bananas, mangoes, coconut palms, oil palms, rubber, pepper, vines, hops, vegetables, cucurbits, tobacco, coffee, tea, rice, soya beans, peanuts, potatoes, sugar beet, cotton, maize, ornamentals, mushrooms, and turf. Application rates for food crops are 1-2.5 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Russetting is possible with flowering ornamentals, apples, and grapes. Some varieties of flowering ornamentals may be injured. Pittosporum foliage is sensitive. Phytotoxicity may be increased with oils or oil-containing substances.
|







