DIMETHOMORPH
    烯酰吗啉 烯酰吗啉
Introduction: Inhibits the formation of the oomycete fungal cell wall. Local systemic fungicide with good protectant and antisporulant activity. Only the (Z)- isomer is intrinsically active, but, because of rapid interconversion of isomers in the light, it has no advantage over the (E)- isomer in practice. Dimethomorph is a fungicide effective against various fungal pathogens including downy mildew, anthracnose, septoria leaf spot, late blight, root rot, crown rot, etc.in vines and other crops
Common name: Dimethomorph
Another name: Dimethomorphe, Acrobat, Akrobat, Forum, Festival C
Chemical name: (EZ)-4-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl]morpholine
Empirical formula: C21H22ClNO4
Structural formula:
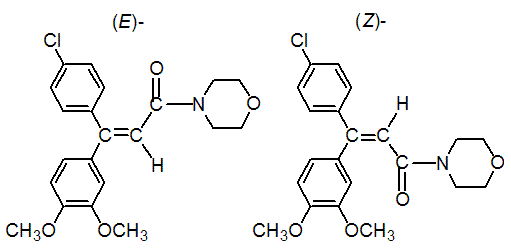
Mol. Weight: 387.86 g/mol
CAS No.: 110488-70-5
Specifications
Leading Dimethomorph supplier
Dimethomorph 50% WDG
Dimethomorph 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Dimethomorph FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 3900 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >4.42 a.i. mg/L. 4) Not irritant to skin (rabbits). 5) Not irritant to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 200 mg/kg diet (9 mg/kg b.w. daily); (1 y) for dogs is 450 mg/kg diet (15 mg/kg daily). Non-oncogenic in 2 y studies in rats and mice.
ADI(JMPR): 0.2 mg/kg b.w. [2007]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 3.4 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >10.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 29.2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low-moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >102 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >32.4 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Dimethomorph's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a fungicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 7.39×10-9 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates dimethomorph will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase dimethomorph will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition.Dimethomorph contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and, therefore, may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, dimethomorph is expected to have no mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 5690. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.0×10-15 atm-cu m/mole. If released into water,dimethomorph is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 27 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Dimethomorph is not expected to undergo hydrolysis in the environment due to the lack of functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. Occupational exposure to dimethomorph may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where dimethomorph is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Fungicide reported by G. Albert et al. (Proc. 1988 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1, 17). Introduced in 1993 by Shell (now BASF AG). Patents: EP 120321; US 5952496. Manufacturers: BASF.
Application: Fungicide effective against Oomycetes, especially Peronosporaceae and Phytophthora spp. (but not Pythium spp.) in vines, potatoes, tomatoes and other crops. Used in combination with contact fungicides, and applied at 2.0-2.5 kg formulated product/ha.
| 






