Iprobenfos



 异稻瘟净
异稻瘟净
Introduction: Iprobenfos is systemic organophosphorous fungicide, which inhibit normal development of the thalli by interfere with the membrane permeability of the cell. Control of leaf and ear blast (Pyricularia oryzae), stem rot (Helminthosporium spp.) and sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani) in rice. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to rice. Injury has been noted on beans, soya beans and aubergines.
Common name: Iprobenfos
Another name: Ricid II; Iprofenfos; Kitazin L; Ricid P; S-BENZYL O,O-DIISOPROPYL PHOSPHOROTHIOATE; Iprobenfos [BSI:ISO]; O,O- Diisopropyl S-benzyl thiophosphate; etc.
Chemical name: S-benzyl O,O-diisopropyl phosphorothioate
Empirical formula: C13H21O3PS
Structural formula:
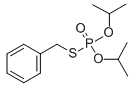
Mol. Weight: 288.34 g/mol
CAS No.: 26087-47-8
Specifications
Leading Iprobenfos supplier
Iprobenfos 95% TC
Iprobenfos 50% EC
Iprobenfos 40% EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Iprobenfos FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H320: Causes eye irritation.
H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
H370: Causes damage to organs.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P337+P313: IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 680 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >4000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 0.34 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Sensitizer (maximization test).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 4.2 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic.
ADI 0-0.3 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R51/53
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Chicken is >705 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Snakehead is 14.7 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >1.2 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 6.05 mg/l. Effects on bees: acute 48 hour LD50 is >37.3 μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: Three metabolites were identified in urine and faeces of rats. Soil: DT50 15d (two soils). Koc 5030. Plant: For metabolism in plants.
Usage: Iprobenfos was introduced by Kumiai Chemical Industry. It is a systemic fungicide to control fungal diseases on rice.
Application: Mode of Action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed through the roots and leaves. Translocation and metabolism in the rice plant have been reported (H. Yamamoto et al., Agric. Biol. Chem., 1973, 37, 1553). Uses Control of leaf and ear blast (Pyricularia oryzae), stem rot (Helminthosporium sigmoideum, Magnaporthe salvinii) and sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani) in rice, applied at 5000-8500 g/ha.







