PIPERONYL BUTOXIDE
  增效醚 增效醚
Introduction: Piperonyl Butoxide is a synthetic derivative of benzodioxole and used as an insecticide synergist, Piperonyl Butoxide enhances the active properties of pyrethrin, pyrethroid, rotenone, and carbamate pesticide ingredients by inhibiting insect microsomal enzyme detoxification activity.
Common name: Piperonyl Butoxide
Another name: Butacide, Butocide, Ethanol butoxide, Pyrenone 606, Butyl carbitol 6-propylpiperonyl ether, 6-Propylpiperonyl butyl diethylene glycol ether, Butoxide (synergist), Piperonylbutoxide, Alleviate, NCI-C02813, FMC 5273, NIA 5273, ENT 14,250, UNII-LWK91TU9AH.
Chemical name: 5-[2-(2-butoxyethoxy)ethoxymethyl]-6-propyl-1,3-benzodioxole
Empirical formula: C19H30O5
Structural formula:
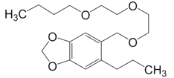
Mol. Weight: 338.438 g/mol
CAS No.: 51-03-6
Specifications
Leading Piperonyl Butoxide supplier
Piperonyl Butoxide 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Piperonyl Butoxide FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400 (91.89%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (94.59%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 4570 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >5.9 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non - irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non - irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Piperonyl butoxide is not carcinogenic to humans. Piperonyl butoxide does not harm the developing fetus. Piperonyl butoxide is not genotoxic.
ADI: 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1995, 2001]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite Quail is >2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Cyprinodon variegatus is 3.94 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour LC50 for Daphnia magna is <1.0 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: Slightly toxicity to honeybees, acute 48 hour LD50 is 25 a.i.μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Piperonyl butoxide's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a synergist for the pyrethrins and related insecticides will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of 5.2×10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates piperonyl butoxide will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase piperonyl butoxide will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 3.6 hours. Particulate-phase piperonyl butoxide will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Piperonyl butoxide contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight; it was rapidly degraded (half-life 8.4 hours) in aqueous solution when illuminated with sunlight. If released to soil, piperonyl butoxide is expected to have moderate to low mobility based upon Koc values ranging from 399-830. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 8.9×10-11 atm-cu m/mole. Piperonyl butoxide is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. A half-life in aerobic soils of 14 days suggests that biodegradation may be an important environmental fate process. If released into water, piperonyl butoxide is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 27 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Piperonyl butoxide is stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, 7 and 9 under sterile, dark conditions. Occupational exposure to piperonyl butoxide may occur through inhalation of dust and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where piperonyl butoxide is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to piperonyl butoxide via inhalation of dust, ingestion of food, and dermal contact with this compound or other insecticide products containing piperonyl butoxide.
Usage: Piperonyl Butoxide was discovered by H. Wachs in 1947 to be used as synergistic agent of pyrethrins, then produced and selled by Mclaughlin Gormley King and other company.
Application: Piperonyl Butoxide is mainly used in combination with insecticides, such as natural pyrethrins or synthetic pyrethroids, in ratios (Piperonyl Butoxide: pyrethrins) ranging from 3:1 to 20:1. It is approved for pre- and postharvest application to a wide variety of crops and commodities, including grain, fruits and vegetables. The application rates are low; the highest single rate is 0.5 lbs Piperonyl Butoxide/acre. It is also used extensively as an ingredient with insecticides to control insect pests in and around the home, in food-handling establishments such as restaurants, and for human and veterinary applications against ectoparasites (head lice, ticks, fleas). A wide variety of water-based Piperonyl Butoxide-containing products such as crack and crevice sprays, total release foggers, and flying insect sprays are produced for and sold to consumers for home use. Piperonyl Butoxide has an important public health role as a synergist used in pyrethrins and pyrethroid formulations used for mosquito control (e.g. space sprays, surface sprays and bed nets). Because of its limited, if any, insecticidal properties, Piperonyl Butoxide is never used alone.
| 






