Oxadixyl
    恶霜灵 恶霜灵
Introduction: Oxadixyl is assumed that it inhibits protein synthesis in fungi, by interference with the synthesis. Oxadixy is in combination with contract Fungicides, for control of Peronosporales, such as downy midews, late blights, and rusts, in vines, Maize, potatoes, tobacco, hops, sunflowers, citrus, fruit and vigetables, and as a seed dressing on cotton, peas, and sunflowers.
Common name: Oxadixyl
Another name: Sandofan; Recoil; Ripost; Wakil; SAN 371F; SAN 371; Oxadixyl [BSI:ISO]; M 10797; etc.
Chemical name: 2-methoxy-N-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl)acet-2',6'-xylidide
Empirical formula: C14H18N2O4
Structural formula:
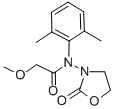
Mol. Weight: 278.3 g/mol
CAS No.: 77732-09-3
Specifications
Leading Oxadixyl supplier
Oxadixyl 96% TC
Oxadixyl 8% + Mancozeb 56% WP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Oxadixyl FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed.
H412 (60%): Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 1860 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 5.6 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a sensitizer.
NOEL: NOEL (1 y) for dogs 500 mg/kg diet; (90 d and lifetime) for rats 250 mg/kg diet. Not teratogenic in rabbits (up to 200 mg/kg b.w. daily) or rats (up to 1000 mg/kg b.w. daily) and no significant effect on reproduction in rats (up to 1000 mg/kg diet). Other Not mutagenic in the Ames, micronucleus and other standard assays.
ADI 0-0.01 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic).
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is 2510 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Goldfish is 300 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 530 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 46 mg/l. Effects on bees: oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 200 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, absorption is rapid and almost complete, with 81-92% eliminated within 144 hours, in the urine and faeces. Extensive metabolism occurs, mainly by hydrolysis at various points on the methoxyacetamide moiety, and oxidation of the methyl group on the phenyl ring to the corresponding alcohol. Similar metabolites are found in soil and in plants. Plants In plants, the major part (>94%) of the applied dosage remains unchanged. A maximum of 9% penetrates the leaf surface after 42 days, and c. 42% of this is metabolised. Soil/Environment In laboratory experiments, DT50 was 6-9 mo. However, in the field, DT50 values of 2-3 mo were observed. In soil, the main metabolite is oxadixyl acid.
Usage: Oxadixyl was introduced by Sandoz AG (now Syngenta AG). It is a fungicide used, in combination with other agents, to control Peronosporales including downy mildew and late blights.
Application: Biochemistry It is assumed that it inhibits protein synthesis in fungi, by interference with the synthesis of ribosomal RNA. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with curative and protective action. Rapidly absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation principally acropetally, but also basipetally and by translaminar movement. Exhibits a synergistic effect with contact fungicides. Uses In combination with contact fungicides, for control of Peronosporales, such as downy mildews, late blights, and rusts, in vines, maize, potatoes, tobacco, hops, sunflowers, citrus, fruit and vegetables, and as a seed dressing on cotton, peas and sunflowers. Application rates for foliar use, 200-300 g/ha.
| 






