Propiconazole
    丙环唑 丙环唑
Introduction: Propiconazole is a systemic foliar fungicide with a broad range of activity.
It is used on grasses grown for seed, mushrooms, corn, wild rice, peanuts, almonds, sorghum,
oats, pecans, apricots, peaches, nectarines, plums and prunes. On cereals it controls diseases
caused by Erysiphe graminis, Leptosphaeria nodorum, Pseudocerosporella herpotrichoides,
Puccinia spp., Pyrenophora teres, Rhynchosporium secalis, and Septoria spp.. Propiconazole's mode
of action is demethylation of C-14 during ergosterol biosynthesis, and leading to accumulation of
C-14 methyl sterols. The biosynthesis of these ergosterols is critical to the formation of cell walls
of fungi. This lack of normal sterol production slows or stops the growth of the fungus, effectively
preventing further infection and/or invasion of host tissues. Therefore, propiconazole is considered
to be fungistatic or growth inhibiting rather than fungicidal or killing.
Common name: Propiconazole
Another name: Banner, Benit, Desmel, Orbit, Radar, Tilt, Fidis, Alamo, Spire, Practis,
Bumper, Mantis, Restore, Banner Maxx, Taspa, Juno, Novel, Break, etc.
Chemical name: (2RS,4RS;2RS,4SR)-1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-propyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-
ylmethyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole
Empirical formula: C15H17Cl2N3O2
Structural formula:
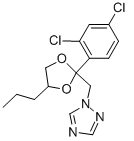
Mol. Weight: 342.22 g/mol
CAS No.: 60207-90-1
Specifications
Leading Propiconazole supplier
Propiconazole 95% TC
Propiconazole 250 g/L EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Propiconazole FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed.
H317 (100%): May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 1517 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is
>4000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5 mg/L (nose only). 4)
Skin irritation: Irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin
sensitization for guinea pig: Sensitizing (Magnusson and Kligman study).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 18 mg/kg/day; (2 y) for mice is 11 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 8.4 mg/
kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.07 mg/kg b.w. [2004]
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22, R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >2510 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h)
for Spot is 2.6 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is
10.2 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 11 day EC50 for Navicula seminulum is 0.093 mg/l.
Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is
>100 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 686 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1×10-6 mm Hg at 25℃ indicates propiconazole will exist
in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase propiconazole will be
degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically- produced hydroxyl radicals; the
half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5.5 hours. Particulate-phase propiconazole
will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Propiconazole has been
reportated to be stable to photolysis. If released to soil, propiconazole has reported soil mobility
ranging from moderate to immobile depending on the organic carbon content of the soil. Propiconazole
is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Volatilization from
water and moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated
Henry's Law constant of 4.1×10-9 atm-cu m/mole.
Usage: Propiconazole was first developed in 1979 by Janssen Pharmaceuticals of Belgium.
It is used agriculturally as a systemic fungicide on turfgrasses grown for seed and aesthetic or
athletic value, wheat, mushrooms, corn, wild rice, peanuts, almonds, sorghum, oats, pecans,
apricots, peaches, nectarines, plums, prunes and lemons. It is also used in combination with
permethrin in formulations of wood preserver.
Application: Mode of Action Propiconazole is absorbed by the assimiliating parts of the plant,
the majority within one hour. It is transported upwards in the xylem. This systemic translocation
contributes to good distribution of the active ingredient within the plant tissue and prevents it
from being washed off. Uses Propiconazole can be used as systemic foliar fungicide with a
broad range of activity, at 100-150 g/ha. On cereals, it controls diseases caused by Cochliobolus
sativus, Erysiphe graminis, Leptosphaeria nodorum, Puccinia spp., Pyrenophora teres,
Pyrenophora tritici-repentis, Rhynchosporium secalis, and Septoria spp. In bananas, control of
Mycosphaerella musicola and Mycosphaerella fijiensis var. difformis. Other uses are in turf against
Sclerotinia homoeocarpa, Rhizoctonia solani, Puccinia spp. and Erysiphe graminis. In rice against
Rhizoctonia solani, Helminthosporium oryzae, and dirty panicle complex. In coffee against Hemileia
vastatrix. In peanuts against Cercospora spp. In stone fruit against Monilinia spp.,
Podosphaera spp., Sphaerotheca spp. and Tranzschelia spp. In maize against Helminthosporium spp.
| 






