THIRAM(TMTD)
 
 
Introduction: Basic contact fungicide with protective action. Protective fungicide applied to foliage to control: Botrytis spp. on grapes, soft fruit, lettuce, vegetables and ornamentals; rust on ornamentals; scab and storage diseases on apples and pears; leaf curl and Monilia on stone fruit. Used in seed treatments alone or in combination with added insecticides or fungicides to control damping-off diseases (e.g. Pythium spp.), and other diseases like Fusarium spp. of maize, cotton, cereals, legumes, vegetables and ornamentals. Also used as a bird repellent.
Common name: Thiram
Another name: Bacteriostat, Disulfide Tetramethylthiuram, Disulfide TMT Nobecutan, Sadoplon 75, Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide, Thiuram, Thiuram D, TMT Disulfide
Chemical name: tetramethylthiuram disulfide
Empirical formula: C6H12N2S4
Structural formula:
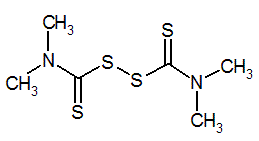
Mol. Weight: 240.43 g/mol
CAS No.: 137-26-8
Specifications
Leading Thiram supplier
Thiram 480 g/L SC
Thiram 50% WP
Thiram 75% WP
Thiram 80% WP
Thiram 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Thiram FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >1800 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 3.46 a.i. mg/L. 4) Moderately irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) May cause sensitisation by skin contact. NOEL (2 y) for rats is 1.5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs is 0.75 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ADI (JMPR): 0.01 mg/kg b.w.[1992]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20/22, R43, R48/22; Xi - Irritant: R36/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Bobwhites quail is >930 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.171 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.139 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is >0.141 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee, Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >106.8 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 540 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Thiram's production and use as a rubber accelerator and as a vulcanizing agent may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. It's use as a fungicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.72×10-5 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates thiram will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase thiram will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 1 hour. Particulate-phase thiram will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Photolysis half lives of 20 days and 4.3 hours have been calculated from measured rate constants for thiram in soil and water, respectively. If released to soil, thiram is expected to have low mobility based upon a Koc of 676. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 3.26×10-7 atm-cu m/mole. Thiram is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Half-lives for thiram measured during soil field studies range from 1 day to 15 weeks. Thiram is expected to undergo biodegradation in soil since this substance has been reported to degrade more rapidly in unsterilized soil than in sterilized soil. If released into water, thiram is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the measured Koc. Biodegradation is expected to be slow in water based on only 2.8% and 30% degradation after 20 days during screening tests that used sewage sludge innocula. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. Measured BCF values of 1.1-4.4 suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. The hydrolysis half-lives measured for thiram at pH 5, pH 7 and pH 9 were 68.5 days, 3.5 days, and 6.9 hours, respectively. Occupational exposure to thiram may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where thiram is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Fungicidal properties described by W. H. Tisdale & A. L. Flenner (Ind. Eng. Chem., 1942, 34, 501). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it), by Bayer AG (who no longer manufacture it), UCB Chemicals, and later by other companies. Manufacturers: Crompton; General Quimica; India Pesticides; Sharda; UCB.
Application: Apples: For control of bitter rot, black rot, Brooks' spot, fly speck, scab, sooty blotch apply 1.5 to 2.25 kg Thiram 75%WP in 1000 litres of water. For control of cedar-apple rust apply 1.5 to 2.25 kg Thiram 75%WP in 1000 litres of water.
Peachs: For the control of scab, apply 1.5 to 2.25 kg Thiram 75%WP in 1000 litres of water. For the control of brown rot (blossom blight, fruit rot) apply 1.5 to 2.25 kg Thiram 75%WP per 1000 litres of water.
Plums: To control plum pockets (Taphrina communis) apply Thiram 75%WP at the rate of 6.72 kg in 1100 – 1700 litres water per hectare.
Celery (in plant beds): For control of early blight, late blight, rhizoctonia and damping-off apply 1.5 kg Thiram 75%WP in 1000 litres of water. Apply 70 to 105 litres per 100 m2 at 3 day intervals.
Sweet potato: For control of stem rot and scurf apply 1.75 kg Thiram 75%WP in 1000 litres of water. Dip roots of sprouts for 30 seconds in the suspension.
Seed treatment: To control seed decay, seedling blight and damping-off apply the following amounts of Thiram 75%WP per 25 kg of seed. Mix seed and Thiram 75%WP thoroughly.
| 






