DIFLUFENICAN
  吡氟酰草胺 吡氟酰草胺
Introduction: A herbicide used to control grasses and broad-leaved weeds often used in mixtures.
Common name: Diflufenican
Another name: Diflufenicanil, etc.
Chemical name: 2',4'-difluoro-2-(α,α,α-trifluoro-m-tolyloxy)nicotinanilide
Empirical formula: C19H11F5N2O2
Structural formula:
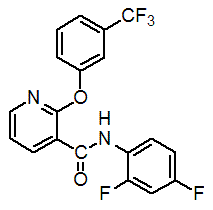
Mol. Weight: 394.29 g/mol
CAS No.: 83164-33-4
Specifications
Leading Diflufenican supplier
Diflufenican 480 g/L EC
Diflufenican 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Diflufenican FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400 (14.29%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H412 (99.47%): Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273 Avoid release to the environment.
P391 Collect spillage.
P501 Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >5.12 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: In 14 d sub-acute trials in rats, no adverse effect observed at 1600 mg/kg b.w. In 90 d feeding trials, NOEL for dogs was 1000 mg/kg b.w. daily, for rats was 500 ppm diet. Non-mutagenic in the Ames test.
ADI: 0.2 mg/kg b.w. [Rat, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available.
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R52, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is >2150 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for carp is >0.099 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >0.24 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.00025 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >112.3 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Plants: In cereals, rapidly metabolised via the nicotinamide and nicotinic acid to CO2. Following pre-emergence application in autumn, no residues are detectable in the grain and straw after c. 200-250 days. Soil/Environment In soil, degradation proceeds via the metabolites 2-(3-trifluoromethylphenoxy)nicotinamide and 2-(3-trifluoromethylphenoxy)nicotinic acid to bound residues and CO2. Half-life varies from 15 to 30 weeks, depending on soil type and water content.
Usage: Herbicide reported by M. C. C. Ramp et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1985, 1, 23) and by C. F. A. Kyndt et al. (ibid., p. 29). Introduced by May & Baker Ltd (now Bayer CropScience). Patents: EP 53011. Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience; Shenyang. Blocks carotenoid biosynthesis, by inhibition of phytoene desaturase.
Application: Selective contact and residual herbicide, absorbed principally by the shoots of germinating seedlings, with limited translocation. Applied at 125-250 g/ha pre- or early post-emergence in autumn-sown wheat and barley, to control grass and broad-leaved weeds, particularly Galium, Veronica and Viola spp. Normally used in combination with isoproturon or other cereal herbicides. Any slight phytotoxicity is in the form of small transient patches on basal leaves, with no adverse effect on crop development.
| 






