BROMOXYNIL
  溴苯腈 溴苯腈
Introduction: An HBN herbicide used for post-emergence control of annual broad-leaved weeds. it is also a pesticide transformation product. Weeds controlled including pigweed, mayweed, knotweed, shepherd's purse, goosefoot, morning glory, dwarf marigold, stinkweed, cocklebur, wild radish, etc. in cereals including wheat, barley, oats; lucerne; corn; sorghum; onions; flax; mint; turf and non-crop land.
Common name: Bromoxynil
Another name: Brominal, Brominil, Broxynil, Sabre, Brittox, Brominex, Buctril, Labuctril, Pardner, Toplan, Chipco buctril, Nu-lawn weeder, Oxytril M, Labuctril 25, ME 4 Brominal, Bromotril, Certrol B, Litarol M, Buctril industrial, Chipco crab-kleen, Butilchorofos, Novacorn, Terset, Butil chlorofos, Brominal Triple, Brominal Plus, Brominal Industrial, Torch, Bucril, Pack, Buctril-atrazine, etc.
Chemical name: 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile
Empirical formula: C7H3Br2NO
Structural formula:
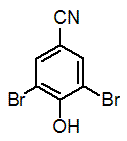
Mol. Weight: 276.9 g/mol
CAS No.: 1689-84-5
Specifications
Leading Bromoxynil supplier
Bromoxynil 97% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Bromoxynil FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H361d: Suspected of damaging the unborn child.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 130 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.15 a.i. mg/L. 4) Not irritant to skin (rabbits). 5) mild irritant to eyes (rabbits). 6) Is a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 20 ppm.
ADI: 0.03 mg/kg b.w./day [Dog, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Reproduction risk category 3: R63; T+ - Very toxic: R26; T - Toxic: R25; Xn - Harmful: R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 217 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is 29.2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 12.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Navicula pelliculosa is 0.12 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low-moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 150 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 10.9 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 45 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Bromoxynil's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a herbicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.28×10-7 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates bromoxynil will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase bromoxynil will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 51 days. Particulate-phase bromoxynil will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Bromoxynil in aqueous solutions photolyzes in sunlight to form 3-bromo-hydroxybenzonitrile (MBBP) and 4-hydroxybenzonitrile, and therefore may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, bromoxynil is expected to have moderate mobility based upon a reported Koc of 302. The pKa of bromoxynil is 3.86, indicating that this compound will exist almost entirely in the anion form in the environment and anions generally do not adsorb more strongly to soils containing organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts. Volatilization from moist soil is not expected because the compound exists as an anion and anions do not volatilize. Bromoxynil may not volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Bromoxynil is rapidly biodegraded by soil microorganisms; the major biodegradation products in soil are 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzamide indicating that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, bromoxynil is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Biodegradation data in water were not available. The pKa indicates bromoxynil will exist almost entirely in the anion form at pH values of 5 to 9 and therefore volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process. An estimated BCF of 28 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. In the moist soil environment, bromoxynil is degraded by hydrolysis and debromination to less-toxic substances such as hydroxybenzoic acid suggesting that hydrolysis may be an important environmental fate process under environmental conditions (pH 5 to 9). Photolysis in sunlit surface waters is expected to be an important environmental fate process for bromoxynil; when buffered bromoxynil solutions were filtered to remove radiation below 300 nm, more than 80% and 60% of the bromoxynil degraded at pH 7.0 and 4.5, respectively. Occupational exposure to bromoxynil may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where bromoxynil is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to bromoxynil via inhalation of ambient air and dermal contact with surface water in the vicinity or agricultural regions where the pesticide is actively being used. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicidal properties of bromoxynil described independently by R. L. Wain (Nature (London), 1963, 200, 28), by K. Carpenter & B. J. Heywood (ibid., p. 28), and by Amchem Products Inc. Development reviewed by B. J. Heywood (Chem. Ind. (London), 1966, p. 1946). Introduced by May & Baker Ltd and by Amchem Products Inc. (both now Bayer CropScience). Patents: GB 1067033 to May & Baker; US 3397054; US 4332613 both to Amchem. Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience Nufarm Ltd; Hesenta; Makhteshim-Agan; Punjab; Sundat; Zhejiang. Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site; also uncouples oxidative phosphorylation.
Application: Selective contact herbicide with some systemic activity. Absorbed by the foliage, with limited translocation. Post-emergence control of annual broad-leaved weeds, especially young seedlings of the Polygonaceae, Compositae, and certain Boraginaceae, in cereals, ryegrass-seed crops, turf, and non-crop land, at rates up to 450 g octanoate/ha; in maize and sorghum, applied at up to 600 g/ha. Often used in combination with other herbicides, to extend the spectrum of control.
| 






