CHLOROTOLURON
  绿麦隆 绿麦隆
Introduction: A contact and residual urea herbicide used to control broad-leaved weeds and grasses including annual meadow grass, black-grass, nightshade, bindweed, chickweed, fat hen, marigold, speedwells, knotgrass, hemp-nettle, dead-nettle, common poppy, mayweed, etc. in cereals including wheat, barley, rye, triticale; potatoes; maize; vegetables including onions, carrot, parsnip; fruit including blackcurrant, apples, pears, chrries, strawberry, gooseberry field.
Common name: Chlorotoluron
Another name: Dicuran, Tolurex, Clortokem, Dikurin, Highuron, Chlortoluron [BSI], Syncuran, Lentipur Forte, etc.
Chemical name: 3-(3-chloro-p-tolyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
Empirical formula: C10H13ClN2O
Structural formula:
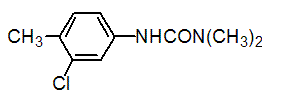
Mol. Weight: 212.68 g/mol
CAS No.: 15545-48-9
Specifications
Leading Chlorotoluron supplier
Chlorotoluron 25% WP
Chlorotoluron 95% TC
Chlorotoluron 97% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Chlorotoluron FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H351: Suspected of causing cancer.
H361d ***: Suspected of damaging the unborn child.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >10000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >5.3 a.i. mg/L. 4) Not irritant to skin (rabbits). 5) Not irritant to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 100 ppm (5 mg/kg daily), mice is 100 ppm (11.3 mg/kg daily).
ADI: 0.04 mg/kg b.w./day [Rat, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; Xn - Harmful: R63; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is 272 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 20 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 67 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.024 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 177.4 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is >1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Chlortoluron's production and use (not marketed in U.S.) as a herbicide may have resulted in its release directly to the environment. If released to the atmosphere, chlortoluron should exist solely in the particulate phase based on an experimental vapor pressure of 3.6×10-8 mm Hg at 25 deg C. Particulate-phase chlortoluron may be physically removed from the air by wet and dry deposition. In soil, measured Koc values averaged from 150-420 with adsorption dependent on the percentage of organic matter present in the soil. These values indicate that chlortoluron will generally have moderate mobility in soil. Biodegradation is expected to be a major fate process for chlortoluron in soil; degradation half-lives range from 4-16 weeks. Monomethyl chlortoluron and N-demethylated chlortoluron were major metabolites of chlortoluron indicating that biodegradation proceeds via cleavage of the C-N bond. Volatilization from moist soil or water surfaces is not expected based on an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.4×10-10 atm-cu m/mol. In water, chlortoluron may adsorb to particulates and organic matter in the water column. Based on soil studies, biodegradation may also be an important fate process in water. Bioconcentration of chlortoluron in aquatic organisms is not expected to be a major fate process with an estimated BCF value of 40. The general population may be exposed to chlortoluron through the ingestion of contaminated drinking water in countries where chlortoluron is used. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicide reported by Y. L'Hermite et al. (C. R. Journ. Etud. Herbic. Conf., COLUMA, 5th, 1969, II, 349). Introduced by Ciba AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents: BE 728267; GB 1255258. Manufacturers: ÉMV; Jingma; Makhteshim-Agan; Nufarm GmbH; Syngenta; Synthesia; United Phosphorus. Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site.
Application: Selective herbicide, absorbed by the roots and foliage. Effective at 1.5-3.0 kg/ha, both as a residual soil-acting herbicide and a contact foliar-spray, against many broad-leaved and grass weeds of winter cereals, especially against Alopecurus myosuroides. It is combined with mecoprop to improve the control of Galium, Papaver and Veronica spp. Phytotoxicity Some varieties of wheat and barley may be injured.
| 






