FOMESAFEN
  氟磺胺草醚 氟磺胺草醚
Introduction: Fomesafen is a pre-emergence herbicide for use in leguminous crops for post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds including pigweed, black nightshade, velvetleaf, cocklebur, etc. in legumes, cotton, soybeans, potatoes, and tomatoes.
Common name: Fomesafen
Another name: Fomesafene, Reflex, UNII-M0A3U4CDTF, Fomesafene [ISO-French], Fomesafen [ANSI:BSI:ISO]
Chemical name: 5-(2-chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-N-mesyl-2-nitrobenzamide
Empirical formula: C15H10ClF3N2O6S
Structural formula:
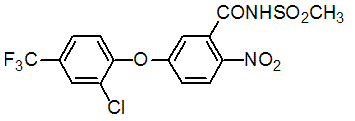
Mol. Weight: 438.76 g/mol
CAS No.: 72178-02-0
Specifications
Leading Fomesafen supplier
Fomesafen 250 g/L SL
Fomesafen 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 1250 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >1000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >4.97 a.i. mg/L. 4) Mild-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Mild to moderate-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a sensitizer (guinea pig). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (18 mo) for mice is 1 mg/kg b.w. daily (liver tumours in mice due to peroxisome proliferation - not relevant to man); (6 mo) for dogs is 1 mg/kg b.w. daily. NOEL: developmental toxicity for rabbits is 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ADI: 0.003 mg/kg b.w./day[UK ACP 1999]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Mallard ducks is 5000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 170 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 330 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is 0.17 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 50 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE Fomesafen's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a herbicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of <3.0×10-8 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates fomesafen will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase fomesafen will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Fomesafen contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, fomesafen is expected to have very high to low mobility based upon Koc values of 34 to 1200, depending on soil type. The pKa of fomesafen is 2.83, indicating that this compound will exist almost entirely in anion form in the environment and anions generally do not adsorb more strongly to soils containing organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts. Volatilization from moist soil is not expected because the acid exists as an anion and anions do not volatilize. Reported biodegradation half-lives for fomesafen of 6 to >12 months under aerobic conditions depending on soil type, and an anaerobic half-life of <3 weeks in soil indicating that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process. If released into water, fomesafen is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon its pKa. A reported BCF of 6 in bluegill suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. Fomesafen will photodecompose readily under relatively low intensities of sunlight. Occupational exposure to fomesafen may occur through inhalation of spray mists or aerosols and dermal contact with this herbicide during or after its application or at workplaces where fomesafen is produced.
Usage: Herbicide reported by S. R. Colby et al. (Proc. Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 10th, 1983, 1, 295). Introduced by ICI Plant Protection Division (now Syngenta AG). Patents: EP 3416. Manufacturers: Sannong; Syngenta. Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor.
Application: Selective herbicide, absorbed by both leaves and roots, with very limited translocation in the phloem. Early post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds in soya beans. Applied at 200-400 g/ha. Non-phytotoxic to soya beans and to other crops such as beans of the genus Phaseolus and the leguminous cover crops Pueraria and Calapogonium.
| 






