Lactofen
  乳氟禾草灵 乳氟禾草灵
Introduction: Lactofen is a member of the diphenyl ether chemical family. It is available in the technical solid form or as an emulsifiable concentrate. It is applied as a foliar spray on target weeds. It is commonly used to control broadleaf weeds in soybeans, cereal crops, potatoes and peanuts. It may commonly be combined with oil or fertilizer adjuvants and/or surfactants. Formulations may contain solvents such as xylenes and cumene.
Common name: Lactofen
Another name: Cobra; Cobra herbicide; Lactofen [ANSI]; PPG 844; etc.
Chemical name:
ethyl O-[5-(2-chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-2-nitrobenzoyl]-DL-lactate
Empirical formula: C19H15ClF3NO7
Structural formula:
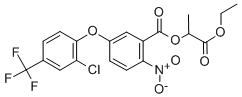
Mol. Weight: 461.80 g/mol
CAS No.: 77501-63-4
Specifications
Leading Lactofen supplier
Lactofen 80% TC
Lactofen 240 g/L EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Lactofen FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302 (57.41%): Harmful if swallowed.
H312 (42.59%): Harmful in contact with skin.
H411 (42.59%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
H413 (55.56%): May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 5.3 a.i.mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Severely irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (1 y) for dogs is 5 mg/kg/day. Other It is unlikely that lactofen would have teratogenic effects in humans under normal conditions.
ADI 0-0.0015 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: NL (Not listed)
EC Risk Classification: Xi - Irritant: R36/37/39; H - Handlings risks: R34
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >2510 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Bluegill sunfish is >0.10 a.i.mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >8.4 a.i.mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >160 a.i.μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
If released to air, a vapor pressure of 7×10-8 mm Hg at 20℃ indicates lactofen will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase lactofen will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically- produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5 days. Particulate-phase lactofen will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Lactofen absorbs light in the environmental UV spectrum and may undergo photolysis; the photodegradation half-life of lactofen was reported as 24 days. If released to soil, lactofen is expected to have no mobility based upon a Koc of 10,000. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 4.2×10-7 atm-cu m/mole. Lactofen is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Lactofen persists in soil for a very short time, with reported half-lives in the range of 1-7 days. The primary degradation product of lactofen is acifluorfen (5-(2-chloro-4-trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)-2-nitrobenzoic acid). If released into water, lactofen is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Hydrolysis is expected to be an important fate process under alkaline conditions based on an estimated hydrolysis half-life of 37 days at pH 8.
Usage: Lactofen was introduced by PPG Industries. It is used for the post-emergence control of weeds in cotton, soybeans and other crops.
Application: Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action Exhibits both pre-emergence and post-emergence activity. Uses Post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds in cotton, soya beans and snap beans, at 0.2 lb/a. Registration for use on peanuts is pending.
| 






