METRIBUZIN
    嗪草酮 嗪草酮
Introduction: A pre- and post-emergence herbicide used to control weeds in soybeans; potatoes; barley, wheat; asparagus; sugarcane; tomatoes; peas; lentils.
Common name: Metribuzin
Another name: Sencor, Lexone, Metribuzine, Zenkor, Sencorex, Senkor, Lexone DF, Sencor DF,Sencoral, Sencorer, etc.
Chemical name: 4-amino-6-tert-butyl-4,5-dihydro-3-methylthio-1,2,4-triazin-5-one
Empirical formula: C8H14N4OS
Structural formula:
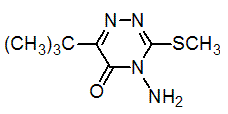
Mol. Weight: 214.29 g/mol
CAS No.: 21087-64-9
Specifications
Leading Metribuzin supplier
Metribuzin 35% WDG
Metribuzin 70% WP
Metribuzin 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Metribuzin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 322 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 2.05 a.i.mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats and dogs is 100, mice c. is 800 mg/kg diet.
ADI: 0.013 mg/kg b.w./day [Rat, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 164 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 74.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 49 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.02 mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 166 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 427 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Metribuzin's use as herbicide is expected to result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 4.35×10-7 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates metribuzin will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase metribuzin will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 21 hrs. Particulate-phase metribuzin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Metribuzin absorbs light in the environmental UV spectrum and has a photolysis half-life of 2.5 days on sandy loam soil irradiated outdoors. If released to soil, metribuzin is expected to have high mobility based upon an average experimental Koc of 60. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon experimental data and an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.2×10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Even though direct photolysis in water and on soil appears to degrade metribuzin rapidly in the laboratory, only metribuzin that is on the surface of soil is affected by direct photolysis. Biodegradation is the primary means of metribuzin dissipation from soils. The half-life is 172 and 439 days for sandy loam under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, respectively. If released into water, metribuzin is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. A BCF of 10 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low.
Usage: Herbicide reported by W. Draber et al. (Naturwissenschaften, 1968, 55, 446) and reviewed by L. Eue (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1972, 25, 175). Introduced by Bayer AG and E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co., and first marketed in 1971. Patents: BE 697083, DE 1795784 both to Bayer; US 3905801 to Du Pont. Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience; DuPont; Feinchemie Schwebda; Rallis. Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Selectivity is due to metabolism (mostly conjugation) within the plant (C. Fedtke, Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1993, 1, 221).
Application: Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed predominantly by the roots, but also by the leaves, with translocation acropetally in the xylem. Pre- and post-emergence control of many grasses and broad-leaved weeds in soya beans, potatoes, tomatoes, sugar cane, alfalfa, asparagus, maize and cereals, at 0.07-1.45 kg/ha. Phytotoxic to many crops, including crucifers, cucurbits, lettuce, onions, sugar beet, sunflowers, flax, strawberries, sweet potatoes, and tobacco.
| 






