NAPROPAMIDE
    敌草胺 敌草胺
Introduction: A soil applied herbicide for pre-emergence control of weeds in a range of crops including oilseed rape, fruit and woody ornamentals.
Common name: Napropamide
Another name: Devrinol, Napropamid, Racemic devrinol, Waylay, Napromide, etc.
Chemical name: (RS)-N,N-diethyl-2-(1-naphthyloxy)propionamide
Empirical formula: C17H21NO2
Structural formula:
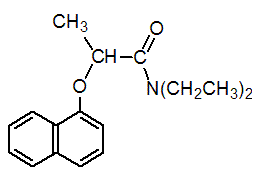
Mol. Weight: 271.36 g/mol
CAS No.: 15299-99-7
Specifications
Leading Napropamide supplier
Napropamide 50% WP
Napropamide 96% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H319 (97.87%): Causes serious eye irritation.
H411 (97.87%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P337+P313: IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >4680 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >4.8 a.i.mg/L. 4) Not a skin irritant (rabbits). 5) Moderate eye irritant (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 30 mg/kg b.w. daily; (90 d) for dogs is 40 mg/kg b.w. daily. Developmental toxicity NOEL for rats and rabbits is 1000 mg/kg b.w. daily; multigeneration study (rats) is 30 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ADI: 0.3 mg/kg. [Rat, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is >2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 6.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 14.3 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 3.4 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 282 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Napropamide's use as a herbicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.72×10-7 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates napropamide will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase napropamide will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 2 hrs. Particulate-phase napropamide will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, napropamide is expected to have moderate to low mobility based upon measured Kocs ranging from 218 to 700. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 8.41×10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Field studies have shown that the half-life of napropamide ranges from 34 days to over 2 years in soils depending upon the field conditions, with both biodegradation and photolysis contributing to its removal. Photodegradation is an important fate process in soil. If released into water, napropamide is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the reported Kocs. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Direct photolysis in sunlit surface waters is expected to be an important environmental fate process based on a photolysis half-life of 57 minutes in a buffered aqueous solution obtained under laboratory conditions. An BCF value of 77 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate. Hydrolysis is not expected to occur due to the lack of hydrolyzable functional groups. Occupational exposure to napropamide may occur through inhalation of dust particles and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where napropamide is produced or used. (SRC).
Usage: Herbicide reported by B. J. van den Brink et al. (Symp. New Herbic., 3rd, 1969, p. 35). Introduced by Stauffer Chemical Co. (now Syngenta AG). Divested to United Phosphorus Ltd. in 1997. Patents: US 3480671; US 3718455. Manufacturers: Gharda; United Phosphorus Ltd. It is a cell division inhibitor.
Application: Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots, with translocation acropetally. Inhibits root development and growth. Pre-emergence control of annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in asparagus, rhubarb, cucurbits, brassicas, oilseed rape, tomatoes, capsicums, potatoes, peas, nuts, fruit trees and bushes (including citrus), vines, strawberries, sunflowers, safflowers, ornamentals, tobacco, olives, figs, mint, turf, and other crops, at 2-6 kg/ha. Phytotoxic to wheat and barley.
| 






