OXADIAZON
    恶草灵, 恶草酮 恶草灵, 恶草酮
Introduction: A pre-emergent or early post-emergent herbicide used to control bindweed and some annual broad-leaved weeds in turf, sports greens & ornamental grass; non-cropped areas including playgrounds, roadsides; cemeteries; ornamental shrubs, vines; trees.
Common name: Oxadiazon
Another name: Ronstar, Oxadiazone, Oxydiazon, Foresite, etc.
Chemical name: 5-tert-butyl-3-(2,4-dichloro-5-isopropoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one
Empirical formula: C15H18Cl2N2O3
Structural formula:
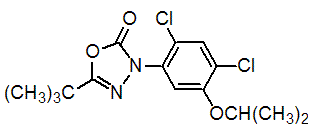
Mol. Weight: 345.2 g/mol
CAS No.: 19666-30-9
Specifications
Leading Oxadiazon supplier
Oxadiazon 120 g/L EC
Oxadiazon 250 g/L EC
Oxadiazon 95% TC
Oxadiazon 96% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >2.77 a.i.mg/L. 4) Negligible irritant to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not sensitising (guinea pig).
NOEL: In 2 y feeding trials, rats and mice receiving 10 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects.
ADI: 0.0036 mg/kg b.w./day[Rat, SF=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Reproduction risk category 3: R62; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >2150 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 1.2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >2.4 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.004 a.img/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >110.5 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Oxadiazon's production and use as a herbicide is expected to result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.15×10-7 mm Hg at 22 deg C indicates oxadiazon will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase oxadiazon will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 16 hours. Particulate-phase oxadiazon will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. There is a potential for the photodegradation of oxadiazon in air; however, the rate at which this may occur is not known. If released to soil, oxadiazon is expected to have only low to slight mobility based upon reported Koc values ranging from 676 to 3,236. In laboratory studies using TLC and column leaching methods, oxadiazon was determined to be immobile in a total of six soils. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 7×10-8 atm-cu m/mole. Oxadiazon is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Oxadiazon photodegrades on soil in natural sunlight with a half-life of 4.65 days. The half-life of oxadiazon in aerobic soil is reported to be 3-6 months. If released into water, oxadiazon is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon reported Koc values. Oxadiazon is stable to hydrolysis at neutral and acidic pHs, but degrades slowly at pH 9, with a half-life of 38 days. Oxadiazon photodegrades in water in natural sunlight with a half-life of 2.65 days. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Biodegradation in aquatic systems is not expected to be an important environmental fate process based on its slow degradation in river die-away tests. BCF values of 24.1-708 in fish suggest that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low to high. Occupational exposure to oxadiazon may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where oxadiazon is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicide reported by L. Burgaud et al. (Symp. New Herbic., 3rd, 1969, p. 201). Introduced by Rhône-Poulenc Agrochimie (now Bayer CropScience). Patents: GB 1110500; US 3385862. Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience; Sannong; Sundat. It is a protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor.
Application: Selective contact herbicide. Pre-emergence control of bindweed, annual broad-leaved weeds and grasses, and post-emergence control of bindweed and annual broad-leaved weeds, in carnations, gladioli, roses, fruit trees and bushes (including citrus), vines, ornamental trees and shrubs, hops, cotton, rice, soya beans, sunflowers, onions, and turf. Effective against mono- and dicotyledonous weeds in rice, at c. 1 kg/ha; in orchards and vineyards, at 2 kg/ha post-em. or 4 kg/ha pre-em. Carnations are tolerant of over-the-top, post-emergence application. Not to be used on red fescue, bentgrass turf, dichronda or centipedegrass.
| 






