Pretilachlor
  丙草胺 丙草胺
Introduction: Pretilachlor is a selective systemic herbicide, absorbed primarily by the germinating shoots, and secondarily by the roots, with trans-location throughout the plant, giving higer concentrations in vegetative parts than in reproductive parts. Used pre-emergence for the control of annual grasses and certain broad-leaved weeds in Rice, both seeded and transplanted fields. It shows selectivity in barley, cotton, peanuts, sugar beet, wheat and several brassica crops. It is to be used in accordance with climatic condition and approval of local authorities.
Common name: Pretilachlor
Another name: Solnet; 2-Chloro-N-(2,6-diethylphenyl)-N-(2-propoxyethyl) acetamide; Rifit; Pretilachlore; etc.
Chemical name: 2-chloro-2',6'-diethyl-N-(2-propoxyethyl)acetanilide
Empirical formula: C17H26ClNO2
Structural formula:
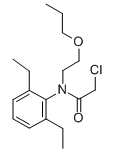
Mol. Weight: 311.85 g/mol
CAS No.: 51218-49-6
Specifications
Leading Pretilachlor supplier
Pretilachlor 95% TC
Pretilachlor 50% EC
Pretilachlor 300 g/L EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Pretilachlor FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed.
H315 (34.72%): Causes skin irritation.
H317 (66.67%): May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H331 (33.33%): Toxic if inhaled.
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P311: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/...
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P332+P313: IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 6099 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >3100 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 2.8 a.i.mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Moderately irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a sensitiser.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats 30, mice 300 ppm; (0.5 y) for dogs 300 ppm. Other Not genotoxic.
ADI 0-0.018 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R43; Xi - Irritant: R38
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is 10000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.9 a.i.mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 13 a.i.mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedesmus acutus is 9.29 a.i.mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 93 a.i.μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 19.23 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Substitution of the chlorine atom for glutathione to form a conjugate. Cleavage of the ether bond to yield an ethyl alcohol derivative. Both metabolites are susceptible to further degradation. Plants Substitution of the chlorine atom to form a conjugate. Cleavage of the ether bond to yield an ethyl alcohol derivative. Hydrolytic and reductive removal of the chlorine atom. Soil/Environment Applied to paddy water, pretilachlor disappeared from the water by adsorption to the soil, where it is rapidly degraded under practical conditions, median DT50 (lab.) 30 d. Due to strong soil adsorption, unlikely to leach.
Usage: Pretilachlor was introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). It is a herbicide used to control the the most common weeds found in paddy rice crops.
Application: Biochemistry Cell division inhibitor; more recent research suggests chloroacetamides may inhibit synthesis of very long chain fatty acids. Mode of action Selective herbicide. It is taken up readily by the hypocotyls, mesocotyls and coleoptiles, and, to a lesser extent, by the roots of germinating weeds. Uses Herbicide effective against main annual grasses, broad-leaved weeds and sedges in transplanted and seeded rice, at 1-1.25 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Applied alone, pretilachlor will cause injury to direct-seeded rice.
| 






