BENZOYLPROP-ETHYL
  新燕灵 新燕灵
Introduction: A selective, post-emergence herbicide that was used for pre-emergence selective control of wild oats in cereals including wheat, barley; beans; cotton; oilseed rape; culinary mustard.
Common name: Benzoylprop-ethyl
Another name: Suffix, BENZOYLPROP ETHYL, Endaven, Suffix 25, etc.
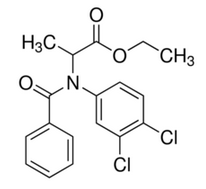
Chemical name: ethyl N-benzoyl-N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-DL-alaninate
Empirical formula: C18H17Cl2NO3
Structural formula:
Mol. Weight: 366.24 g/mol
CAS No.: 22212-55-1
Specifications
Leading Benzoylprop-ethyl supplier
Benzoylprop-ethyl 200 g/L EC
Benzoylprop-ethyl 96% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for mouse: 716 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >1000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rat: 26.8 a.i.mg/L. 4) Non-Irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
Not mutagenic in Ames Test. No evidence of carcinogenicity in animal studies (when indicated) IARC: No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC. Animal testing did not show any effects on fertility.
Classification:
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for duck is >200 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is 0.494 a.i.mg/L.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
The degradation of (14C) benzoylprop ethyl (Suffix, ethyl N-benzoyl-N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-aminoprop ionate) in four soils has been studied under laboratory conditions. The major degradation product of benzoylprop ethyl at up to 4 months after treatment was its corresponding carboxylic acid. On further storage this compound became firmly bound to soil before it underwent a slow debenzoylation process which led to the formation of a number of products including N-3,4-dichlorophenylalanine, benzoic acid, 3,4-dichloroaniline (DCA), which was mainly present complexed with humic acids, and other polar products. Although these polar products were not identified, they were probably degradation products of DCA, since they were also formed when DCA was added to soil. No 3,3',4,4'-tetrachloroazobenzene (TCAB) was detected in any of the soils at limits of detectability ranging from 0.01-0.001 ppm. Since N-3,4-dichlorophenylalanine and 3,4-dichloroaniline were transient degradation products of benzoylprop ethyl, the metabolism in soil of radio-labeled samples of these compounds was also studied. In these laboratory experiments the persistence of the herbicide increased as the organic matter content of the soil increased and the time for depletion of half of the applied benzoylprop ethyl varied from 1 week in sandy loam and clay loam soils to 12 weeks in peat soil.
Usage: Herbicide developed by Shell Research Limited. Patents: BP1164160. A selective, post-emergence herbicide.
Application: Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed predominantly by the roots, but also by the leaves, with translocation acropetally. Used mainly against wild oats in winter and spring wheat field at dosage of 0.9-1.5 kg/ha.
| 






