Thiocyclam-hydrogenoxalate
    杀虫环 杀虫环
Introduction: Thiocyclam-hydrogenoxalate is a broad spectrum insecticide used to control sucking and chewing pests including spidermites, caterpillars, thrips, plant hoppers, whiteflies, wooly aphids on a variety of crops such as oilseed rape, ornamentals including roses, onions, apples and pears.
Common name: Thiocyclam-hydrogenoxalate
Another name: Evisect, Thiocyclam oxalate, Evisekt, Evisect S, Thiocyclam oxalate [ISO], Thiocyclam (ethanedioate 1:1), 5-Dimethylamino-1,2,3-trithiane hydrogen oxalate, Bis(1,2,3-trithiacyclohexyldimethylammonium) oxalate, v-Trithiane, 5-(dimethylamino)-, oxalate, Thiocyclamhydrogenoxalate
Chemical name: N,N-dimethyltrithian-5-amine;oxalic acid
Empirical formula: C7H13NO4S3
Structural formula:
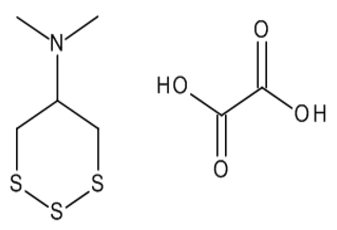
Mol. Weight: 271.37 g/mol
CAS No.: 31895-22-4
Specifications
Leading Thiocyclam-hydrogenoxalate supplier
Thiocyclam-hydrogenoxalate 50% SP
Thiocyclam-hydrogenoxalate 50% WP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 399 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: 1000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: ˃4.5 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No mutagenic in vitro and in vivo mutagenicity assays. Not carcinogenic(rat and mouse). Not toxic on reproduction. Not teratogenic(rat and rabbit).
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II ( Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22, R43; Xi - Irritant: R36, R38
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Japanese quail is 3.45 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for rainbow trout is 0.04 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 2.01 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 3.3 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 11.9 a.i.μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Plants Degradation in plants is the same as in soil. Soil/Environment Thiocyclam hydrogen oxalate, via nereistoxin and its oxide, is broken down to smaller fragments. Degradation is accelerated by light. DT50 in soil 1 d (o.c. 2.8%, pH 6.8, 22℃).
Usage: History Insecticide reported by W. Berg & H. J. Knutti. Its hydrogen oxalate was introduced by Sandoz Agro AG (later Syngenta AG, who sold rights to Arysta LifeScience Corp. and Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd in 2002). Patents DE 2039555 Manufacturers Nippon Kayaku; Sundat.
Application: Biochemistry Analogue or propesticide of the natural toxin nereistoxin. Nicotinergic acetylcholine blocker, causing paralysis by ganglionic blocking action on the central nervous system. Mode of action Selective insecticide with contact and stomach action. Limited systemic activity, with translocation acropetally. Control of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, some Diptera and Thysanoptera. In potatoes for Colorado potato beetle, in rape for Coleoptera and Lepidoptera pest complexes, in irrigated rice for stem borers and some other pests, in maize for corn borer and Tanymecus, in sugar beet for sugar beet weevil and other Coleoptera, in sugar cane for sugar cane stem borer, in fruit trees for Lepidoptera, in vegetables for leaf miners, and various Lepidoptera and Coleoptera.
| 






