Cyprodinil
    嘧菌环胺 嘧菌环胺
Introduction: Cyprodinil is a new fungicide for the control of a broad spectrum of plant diseases. Control of major cereal diseases and of Botrytis cinerea ssp. on grapes and vegetables are the major strengths of cyprodinil. The careful analysis of physico-chemical properties of certain sulfonylureas and the consistent testing of all compounds as fungicides, herbicides and insecticides led to the discovery of the class of compounds and led to cyprodinil. Aspects of chemistry, structure activity considerations, ecological and safety assessments are presented to demonstrate the unique properties of cyprodinil which make it a versatile new tool for the management of plant diseases.
Common name: Cyprodinil
Another name: 4-Cyclopropyl-6-methyl-N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine; 4-Cycloprop yl-6-methyl-N-phenyl-2-pyrimidinamine; Unix; HSDB 7019; Chorus; Chorus 75WG; etc.
Chemical name: 4-cyclopropyl-6-methyl-N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine
Empirical formula: C14H15N3
Structural formula:
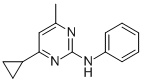
Mol. Weight: 225.29 g/mol
CAS No.: 121552-61-2
Specifications
Leading Cyprodinil supplier
Cyprodinil 98% TC
Cyprodinil 75% WDG
Cyprodinil 50% WDG
Cyprodinil 30% SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Cyprodinil FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H315 (18.11%): Causes skin irritation.
H317 (100%): May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H319 (18.11%): Causes serious eye irritation.
H332 (36.22%): Harmful if inhaled.
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P332+P313: IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P362: Take off contaminated clothing.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >1.2 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Sensitizing (maximization test).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 2.7 mg/kg/day; (18 m) for mice is 196 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 66 mg/kg/day. Other No carcinogenicity in mice and rats. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.03 mg/kg b.w. [2003]
Classification:
WHO Classification: III - company classification (Slightly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III, IV (Caution - Slightly toxic, Caution - Not acutely toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >500 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 2.41 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.22 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 2.6 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >784 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 112.5 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 192 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration, cyprodinil is rapidly absorbed and almost completely eliminated with urine and faeces. Metabolism proceeds by 4-hydroxylation of the phenyl and 5-hydroxylation of the pyrimidine rings, followed by mono- or di-sulfation. Residues in tissues were generally low and there was no evidence for accumulation or retention of cyprodinil or its metabolites. Plants Metabolism proceeded mainly via hydroxylation of the 6-methyl group of the pyrimidine ring, as well as hydroxylation of the phenyl and pyrimidine rings, followed by sugar conjugation. Soil/Environment In soil, the compound dissipated with DT5020-60 d at normal soil humidities and soil temperatures, whereby formation of bound residues represents the major route for dissipation. In leaching and adsorption/desorption experiments, the compound proved to be immobile in soil. Photolytic DT50 in water 13.5 d.
Usage: Cyprodinil was introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). It is a broad spectrum foliar fungicide used to control a range of pathogens mainly on fruit.
Application: Biochemistry Proposed inhibitor of the biosynthesis of methionine and the secretion of fungal hydrolytic enzymes. There is no cross resistance to benzimidazoles, carbamates, dicarboximides, imidazoles, morpholines, quinolines, strobilurins or triazoles. Mode of action Systemic product, with uptake into plants after foliar application and transport throughout the tissue and acropetally in the xylem. Inhibits penetration and mycelial growth both inside and on the leaf surface. Uses As a foliar fungicide for use in cereals, grapes, pome fruit, stone fruit, strawberries, vegetables, field crops and ornamentals; and as a seed dressing on barley. Controls a wide range of pathogens, such as Tapesia yallundae and T. acuformis, Erysiphe spp., Pyrenophora teres, Rhynchosporium secalis, Botrytis spp., Alternaria spp., Venturia spp. and Monilinia spp., at 150-750 g/ha.
| 






