Tebufenozide
    虫酰肼 虫酰肼
Introduction: Tebufenozide is an ecdysone insecticide, which causes the premature molting of insects by interfering with the normal development of insects. It has high insecticidal activity and high selectivity, being effective in treatment of all lepidopteran larvae, caterpillar, diamondback moth and beet armyworm. It has a strong ovicidal activity, being safe to non-target organisms. Tebfenozide has no irritating effect on the eyes and skin without any teratogenic, carcinogenic and mutagenic effects on higher animals, being of high safety to mammals, birds and natural enemies. It is an ideal insecticide during integrated control.
Common name: Tebufenozide
Another name: Tebufenozide [ISO]; N-tert-Butyl-N'-(4-ethylbenzoyl)-3,5- dimethylbenzohydrazide; Confirm; UNII-TNN5MI5EKF; etc.
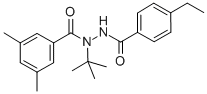
Chemical name: N-tert-butyl-N'-(4-ethylbenzoyl)-3,5-dimethylbenzohydrazide
Empirical formula: C22H28N2O2
Structural formula:
Mol. Weight: 352.47 g/mol
CAS No.: 112410-23-8
Specifications
Leading Tebufenozide supplier
Tebufenozide 95% TC
Tebufenozide 25% SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Tebufenozide FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >4.3 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (2 y) for male rats is 4.8mg/kg/day, for female rats is 6.1 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 1.8 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not mutagenic. Not teratogenic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.013 mg/kg b.w. [1996, 2001, 2003]
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R51, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 (8 d) for Bobwhite quail is >2150 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Bluegill sunfish is 3.0 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 3.8 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.23 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >234 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In the rat, 16 whole-molecule metabolites are formed as a result of oxidation of the alkyl substituents of the aromatic rings, primarily at the benzylic positions. Plants In apples, grapes, rice and sugar beet, the major component is unchanged tebufenozide. Metabolites which are detected in small amounts result from oxidation of the alkyl substituents of the aromatic ring, primarily at the benzylic positions. Soil/Environment Metabolic DT50 in soil 7-66 d (7 soil types); for aerobic, aquatic soil 100 d (25℃, 3 soil types); for anaerobic, aquatic metabolism 179 d (25℃, silt loam). DT50 for field dissipation 4-53 d (12 sites). Koc 351-894. Field dissipation studies indicate no mobility below 30 cm.
Usage: Tebufenozide was developed in USA by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences). It is an insecticide used to control Lepidopterous larvae in a wide variety of cropping situations.
Application: Biochemistry Ecdysone agonist which acts by binding to the receptor site of the insect moulting hormone, ecdysone. Mode of action Lethally accelerates moulting process. Uses Control of lepidopteran larvae on rice, fruit, row crops, nut crops, vegetables, vines, and forestry, generally at 0.06-0.3 lb/a.
| 






