THIAMETHOXAM



 噻虫嗪
噻虫嗪
Introduction: Thiamethoxam is a broad spectrum insecticide, systemic with contact and stomach action. It can be used to control a wide range of common pests such as aphids, whiteflies, thrips, lacewings, leafhoppers, mealybugs, wireworms, ground beetles, fire & carpenter ants, craneflies, mole crickets on turf grass & sod farms, landscape plants, ornamentals.
Common name: Thiamethoxam
Another name: 3-[(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)methyl]-5-methyl-N-nitro-1,3,5-oxadiazinan-4-imine, N-[3-[(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)methyl]-5-methyl-1,3,5-oxadiazinan-4-ylidene]nitramide, n-(3-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)-5-methyl-1,3,5-oxadiazinan-4-ylidene)nitramide
Chemical name: (EZ)-3-(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl)-5-methyl-1,3,5-oxadiazinan-4-ylidene(nitro)amine
Empirical formula: C8H10ClN5O3S
Structural formula:
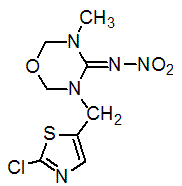
Mol. Weight: 291.71 g/mol
CAS No.: 153719-23-4
Specifications
Leading Thiamethoxam supplier
Thiamethoxam 10% WDG
Thiamethoxam 25% WDG
Thiamethoxam 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Thiamethoxam FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >1563 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >3.72 a.i. mg/L. 4) Slightly Irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Minimally Irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Classified as "not likely to be carcinogenic in humans" based on lifetime studies in mice and rats. Not teratogenic in rats or rabbits. No effects on reproduction.
ADI(JMPR): 0.08 mg/kg b.w. [2010]
Classification:
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50/53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is 576 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >125 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.024 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.005 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Thiamethoxam's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 4.95×10-11 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates thiamethoxam will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase thiamethoxam will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition.Thiamethoxam contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm, and therefore may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, thiamethoxam is expected to have high mobility based upon a average Koc of 68.4. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 4.6×10-15 atm-cu m/mole. Thiamethoxam may not volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Biodegradation data in soil and water were not available. If released into water,thiamethoxam is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Thiamethoxam is stable under acidic conditions but does hydrolyze under alkaline conditions. Occupational exposure to thiamethoxam may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces wherethiamethoxam is produced or used. (SRC).
Usage: Discovered by Ciba (now Syngenta AG) in 1991. Reported by R. Senn et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1998, 1, 27). Introduced in New Zealand in 1997. Manufacturers: Syngenta
Application: Biochemistry Agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, affecting the synapses in the insect central nervous system. Insecticide with contact, stomach and systemic activity. Rapidly taken up into the plant and transported acropetally in the xylem. Uses For control of aphids, whitefly, thrips, ricehoppers, ricebugs, mealybugs, white grubs, Colorado potato beetle, flea beetles, wireworms, ground beetles, leaf miners and some lepidopterous species, at application rates from 10 to 200 g/ha (R. Senn et al., loc. cit.). Major crops for foliar and soil treatments are cole crops, leafy and fruity vegetables, potatoes, rice, cotton, deciduous fruit, citrus, tobacco and soya beans; for seed treatment use, maize, sorghum, cereals, sugar beet, oilseed rape, cotton, peas, beans, sunflowers, rice and potatoes. Also for control of flies in animal and public health, such as Musca domestica, Fannia canicularis, and Drosophila spp.







