Fenthion
    倍硫磷 倍硫磷
Introduction: Fenthion is a contact and stomach organophosphate insecticide used against many sucking, biting pests, especially fruit flies, stem borers, mosquitoes, and Eurygaster cereal bugs. In mosquitoes, it is toxic to both the adult and immature forms (larvae). Once used extensively in the U.S. for controlling intestinal worms, fenthion no longer has FDA approval due to poisoning deaths. Fenthion is available in dust, emulsifiable concentrate, granular, liquid concentrate, spray concentrate, ULV, and wettable powder formulations. While it is effective as an insecticide, it is also moderately toxic to mammals, and highly toxic to birds. Based on its high toxicity to birds, fenthion is used in various parts of the world for weaver bird control. Pest control operators have used it to control pigeons around public buildings, as well. For bird control, use is made of fenthion's contact action and its ready absorption through the skin. It is applied as a paste to roosting areas when utilized for such purposes.
Common name: Fenthion
Another name: Mercaptophos; Baytex; 55-38-9; Lebaycid; Fenthione; Mercaptophos, etc.
Chemical Name (IUPAC): O,O-dimethyl O-4-methylthio-m-tolyl phosphorothioate
Structural formula:
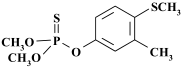
Empirical formula: C10H15O3PS2
Mol. Weight: 278.33
CAS No.: 55-38-9
Specifications
Leading Fenthion supplier
Fenthion 90% TC
Fenthion 50% EC
Packing
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Fenthion FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H331: Toxic if inhaled.
H341: Suspected of causing genetic defects.
H372: Causes damage to organs (central nervous system) through prolonged or repeated exposure if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P284: Wear respiratory protection.
P308 + P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local regulation.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 80, 82 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 250 mg/kg. 2) Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats is 586 mg/kg, female rats is 800 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 for rats is 0.5 mg/l air (aerosol). 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
NOEL: NOEL(2 y) for rats is 0.15 mg/kg diet, for mice is 2 mg/kg diet. Other No carcinogenic effects were observed in other two-year feeding studies of rats and mice.
ADI (JMPR) 0.007 mg/kg b.w. [1995, 1997].
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R23, R48/25, R68; Xn - Harmful: R21/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53.
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic).
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 7.2 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.8 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.0057 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedemus subspicatus is 1.79 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute (48 h) LD50 is >0.308 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 375 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In mammals, following oral administration, elimination is mainly in the form of hydrolysis products in the urine. Major metabolites are fenthion sulfoxide, fenthion sulfone and their oxygen analogues. These metabolites are hydrolysed in further degradation, forming the corresponding phenols. Plants In plants, fenthion is oxidised to the sulfoxide and sulfone, both of which possess insecticidal properties, and to the monodesmethyl compound of fenthion sulfoxide. Further degradation occurs to the sulfone phosphate, which undergoes hydrolysis. Soil/Environment Koc 1500 (Ware, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 123 (1992)). In sediment/water system with and without plants, DT50 is c. 1.5 d (O'Neill et al., Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 8, 759-768 (1989)). The degradation of fenthion occurs rapidly under aerobic conditions, forming the metabolites fenthion sulfoxide, fenthion sulfone, followed by the analogous phenol compounds.
Usage: Fenthion was developed by Bayer Crop Science. Fenthion is a contact and stomach insecticide used against many biting insects. It is particularly effective against fruit flies, leaf hoppers, cereal bugs, stem borers, mosquitoes, animal parasites, mites, aphids, codling moths, and weaver birds. It has been widely used in sugar cane, rice, field corn, beets, pome and stone fruit, citrus fruits, pistachio, cotton, olives, coffee, cocoa, vegetables, and vines.
Application: Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Insecticide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Uses Control of fruit flies, leafhoppers, leaf miners, leaf-eating larvae, stem borers, cereal bugs, and other insect pests in fruit (including citrus), vines, olives, vegetables, cotton, tea, sugar cane, rice, beet, tobacco, ornamentals, etc. For agricultural uses, application rates vary from 60 to 1200 g/ha, depending on crop, pest, pest stage and application method. Control of insect pests (flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches, fleas, ants, ticks, lice, etc.) in public health situations and animal houses, and control of animal ectoparasites. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as recommended.
|







